-BODIES-

Planet
A planet is a large celestial body that orbits one (or more) stars. A planet usually orbits in a circular orbit around the center of its system.

Star
A star is a huge ball of hydrogen and helium plazma. In our solar system the star is known as the "sun".
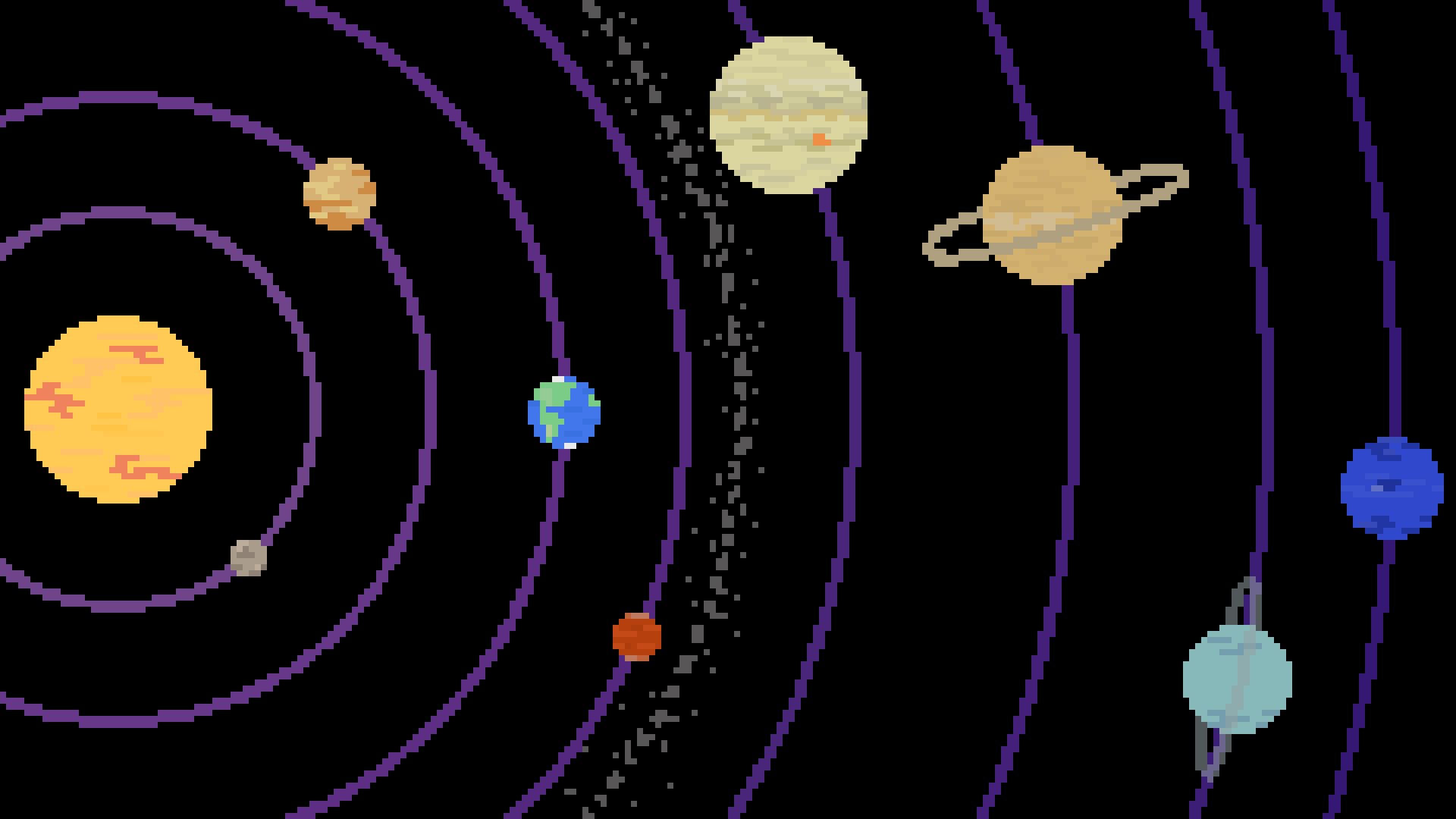
Solar System
A solar system is a colection of stars, planets, dwarph planets, moons, and space rocks held together by gravity. Our solar system has 1 star and 8 planets.
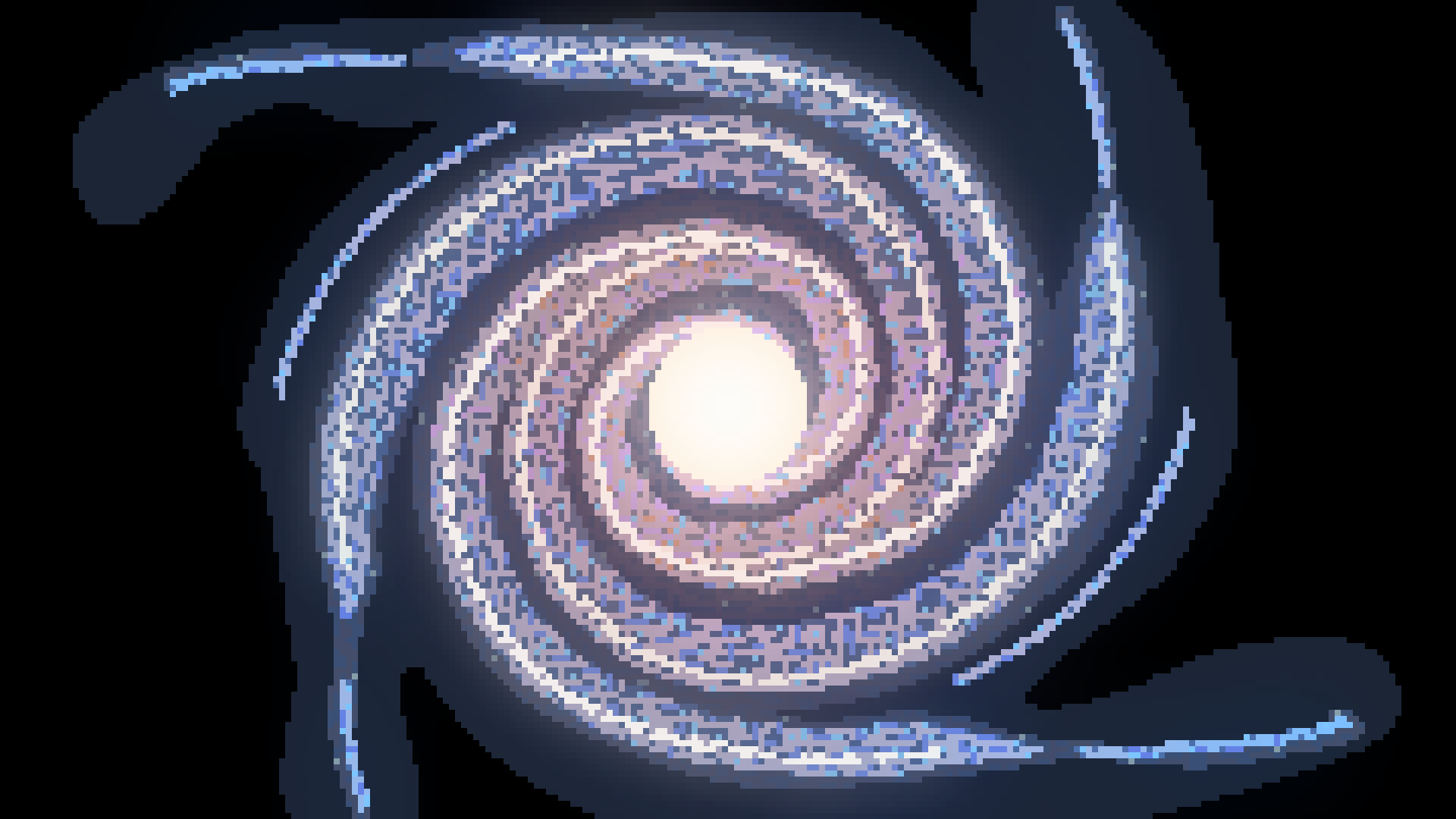
Galaxy
A galaxy is a collection of stars, gas, and dust that are all bound together by gravity. Galaxies can be spiral, eliptical, or irregular and contain up to hundreds of billions of stars.

Moon
A moon is a celestial body that orbits a planet. Most moons are only large asteroids, however some can be larger than planets.

Asteroid
Asteroids are large space rocks that orbit the center of their solar system. They don't have enough mass to force themselves into a sphere.

Meteor
Rocks in space that are smaller than asterods. Meteoroids are in space, meteors are meteoroids when they burn up in Earths atmosphere, and meteorites are meteors that survive and land on Earth's surface.
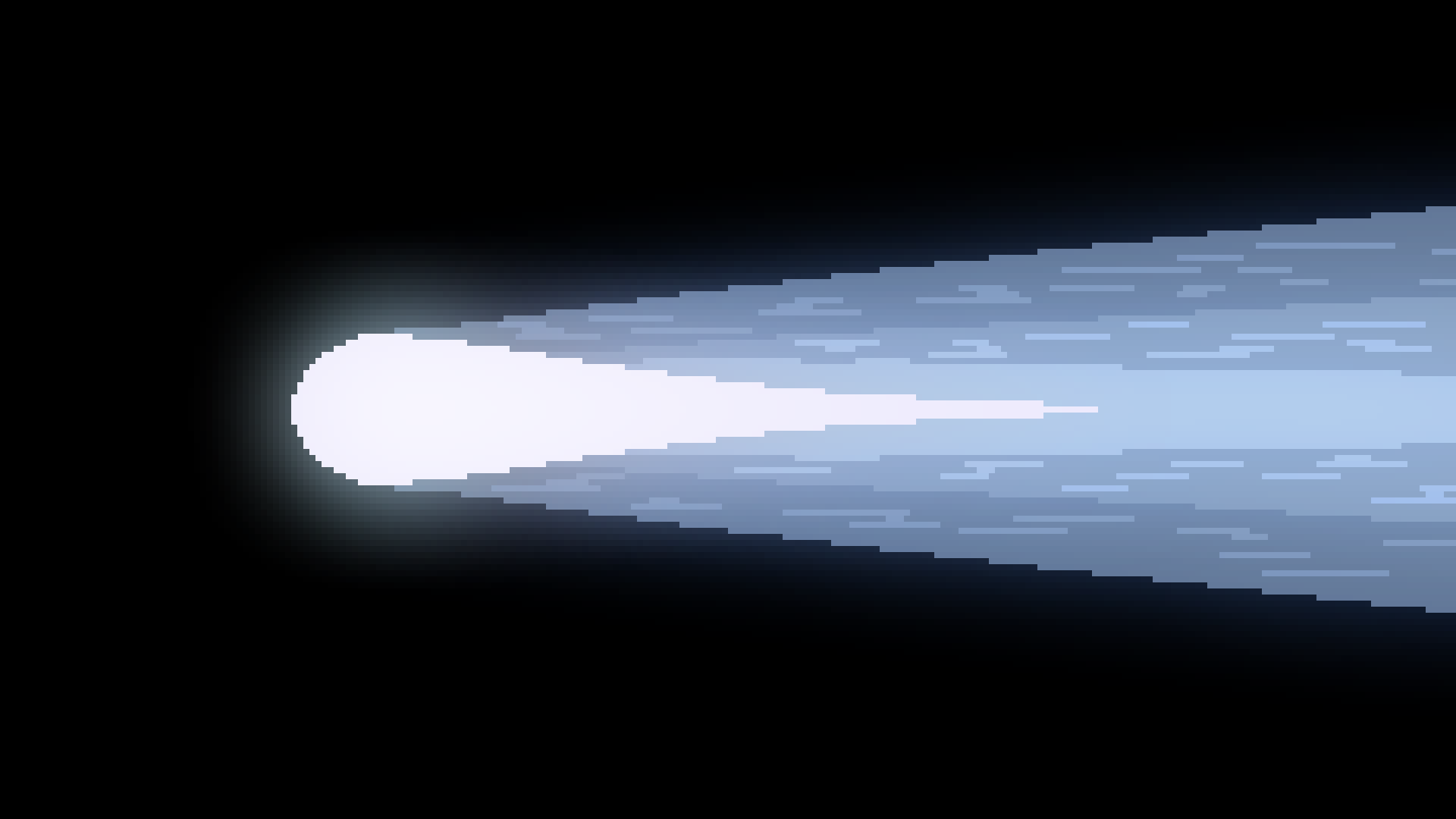
Commet
Commets are specs of ice that soar through space, often times very far from the center of the solar system. They have tails that are caused by solar wind.

Astroid Belt
Astroid belts are loops in a solar system made up of asteroids, meteorites, and dwarph planets.

Protostar
A protostar is a newborn star. In the early years of a solar system, there is a lot of gas and dust orbiting the protostar called a protoplanitary disk. In time, this gas and dust will accumulate into planets and other large bodies.
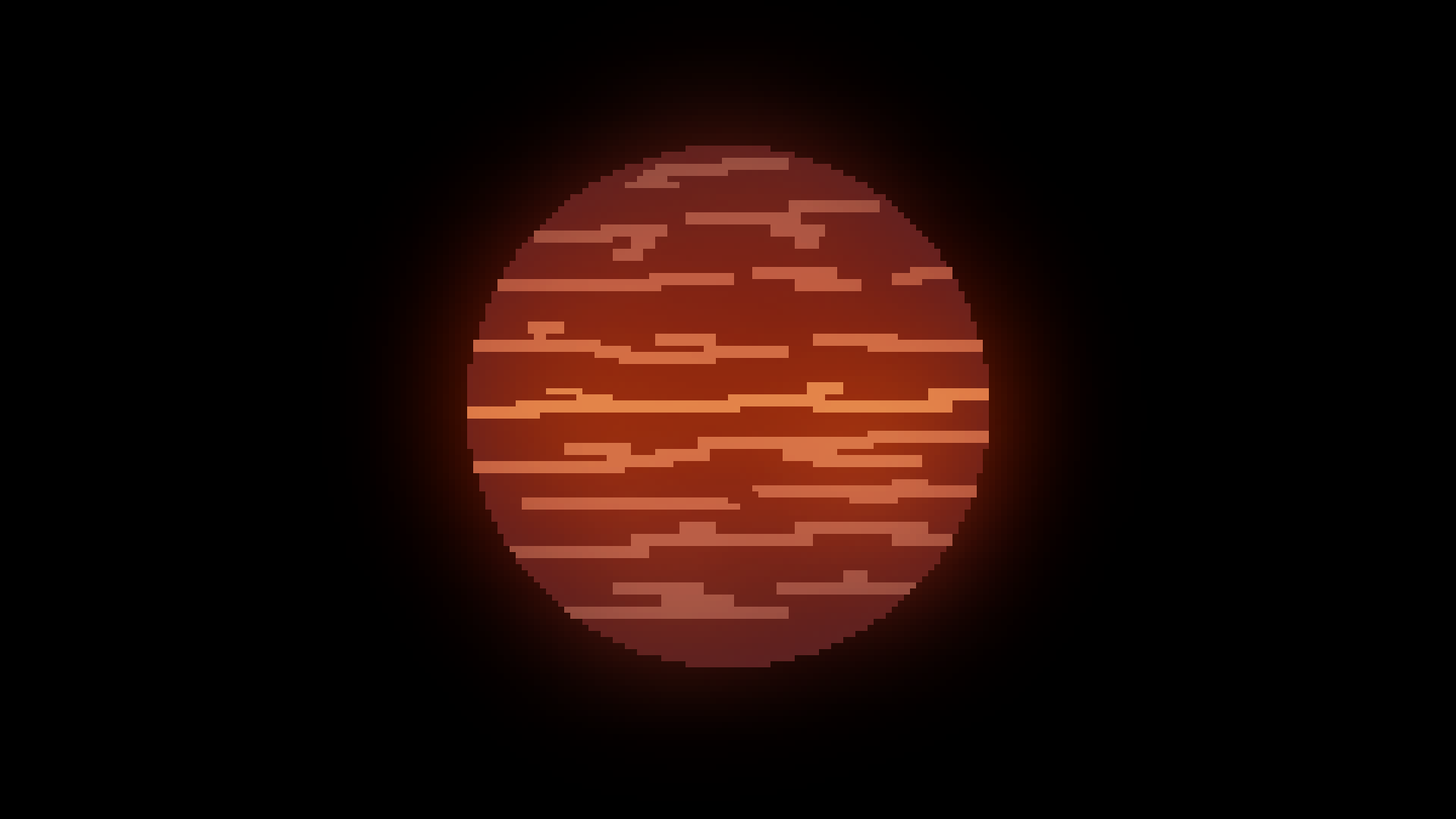

Brown
Dwarph
Dwarph
A brown dwarph star is a ball of hydrogen plazma that has a lot of mass, but not enough to become a star. It is often consitered to be a failed star. It is still usually the center of its solar system.
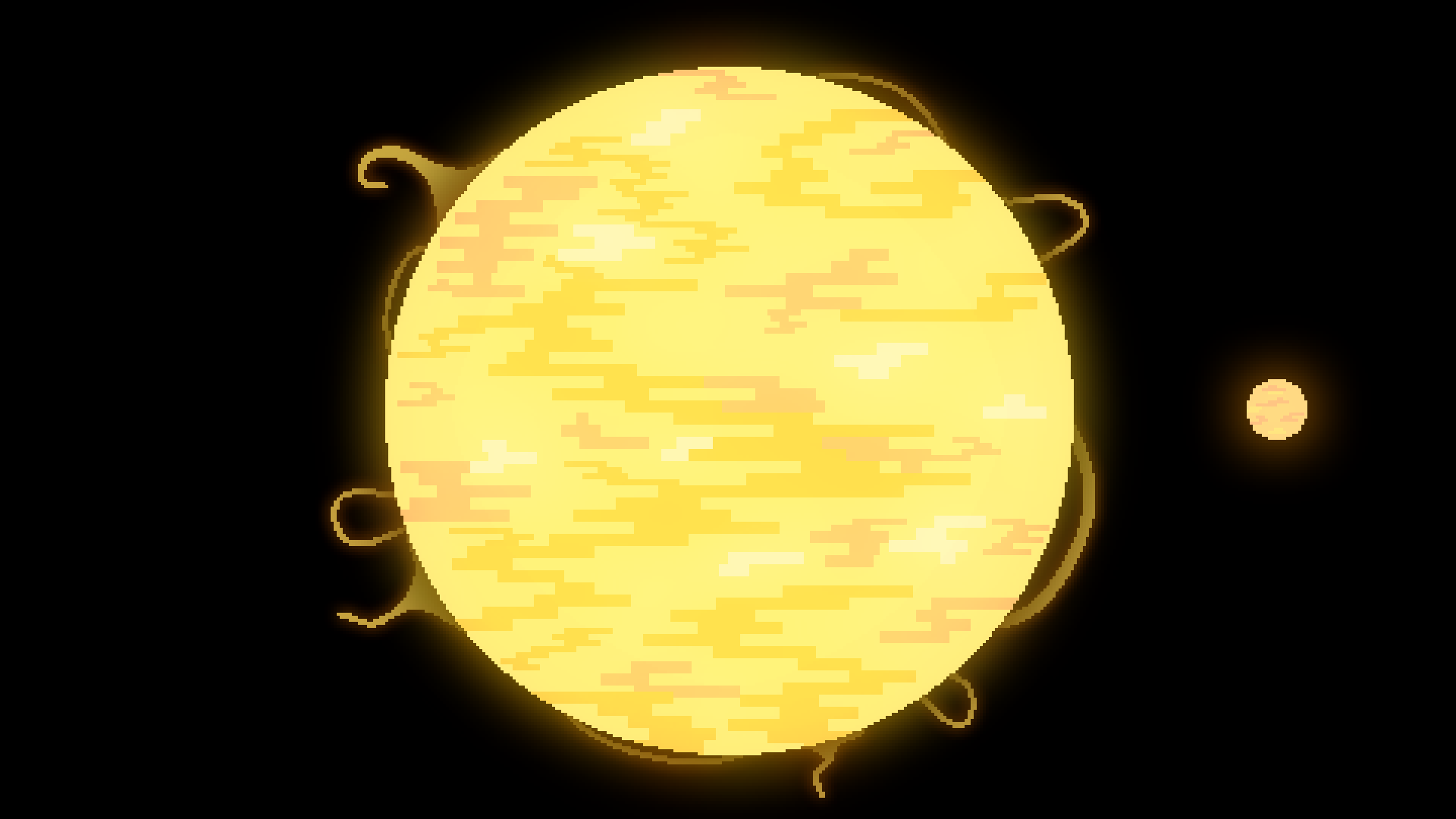

Giant Star
When a star enters the later parts of its life, it becomes very big. More massive stars become super-giants or hyper-giants.
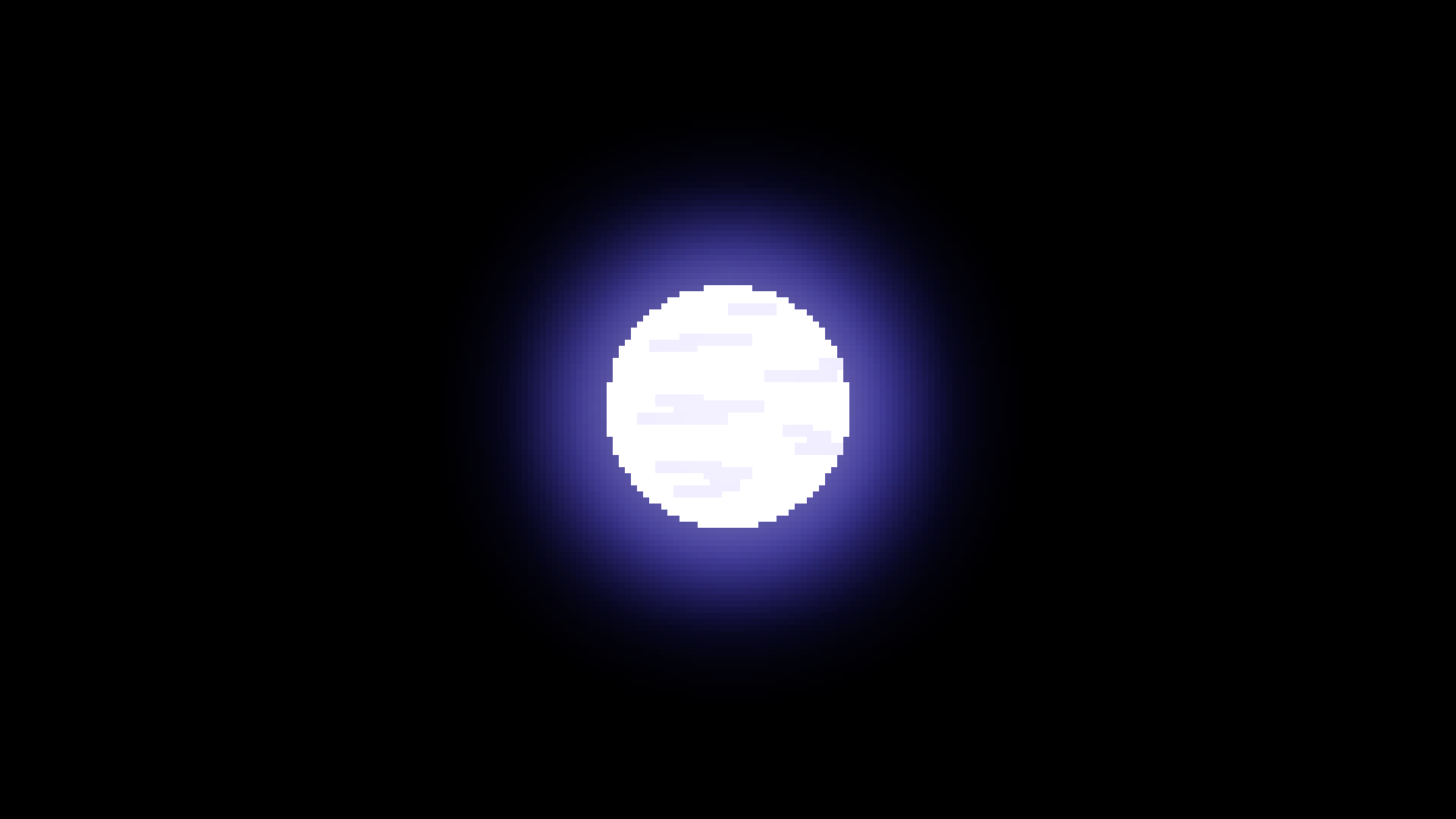

White
Dwarph
Dwarph
When a star about the size of our sun dies, it expells all gas in its outer layers, and leaves only its core. That core is known as a white dwarph and is about the size of the Earth.
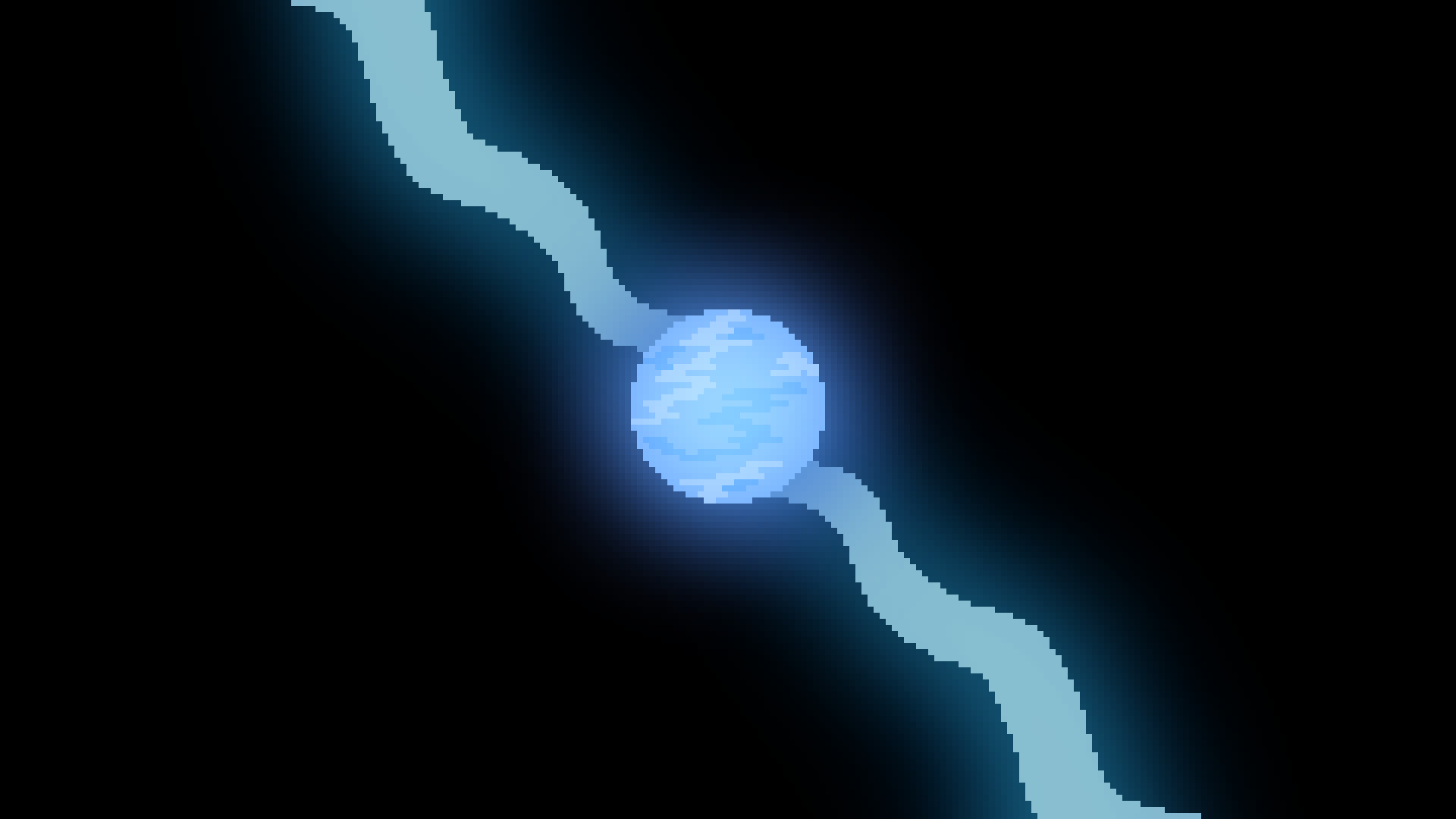

Neutron Star
When a star about 8 times as massive as the sun implodes, its core is condenced into the size of NYC. This super dence star is known as a neutron star. Some are known as pulsars if they produce jets of radiation and spin (looking like pulses to us), and magnetars if they have a strong electro-magnetic field.
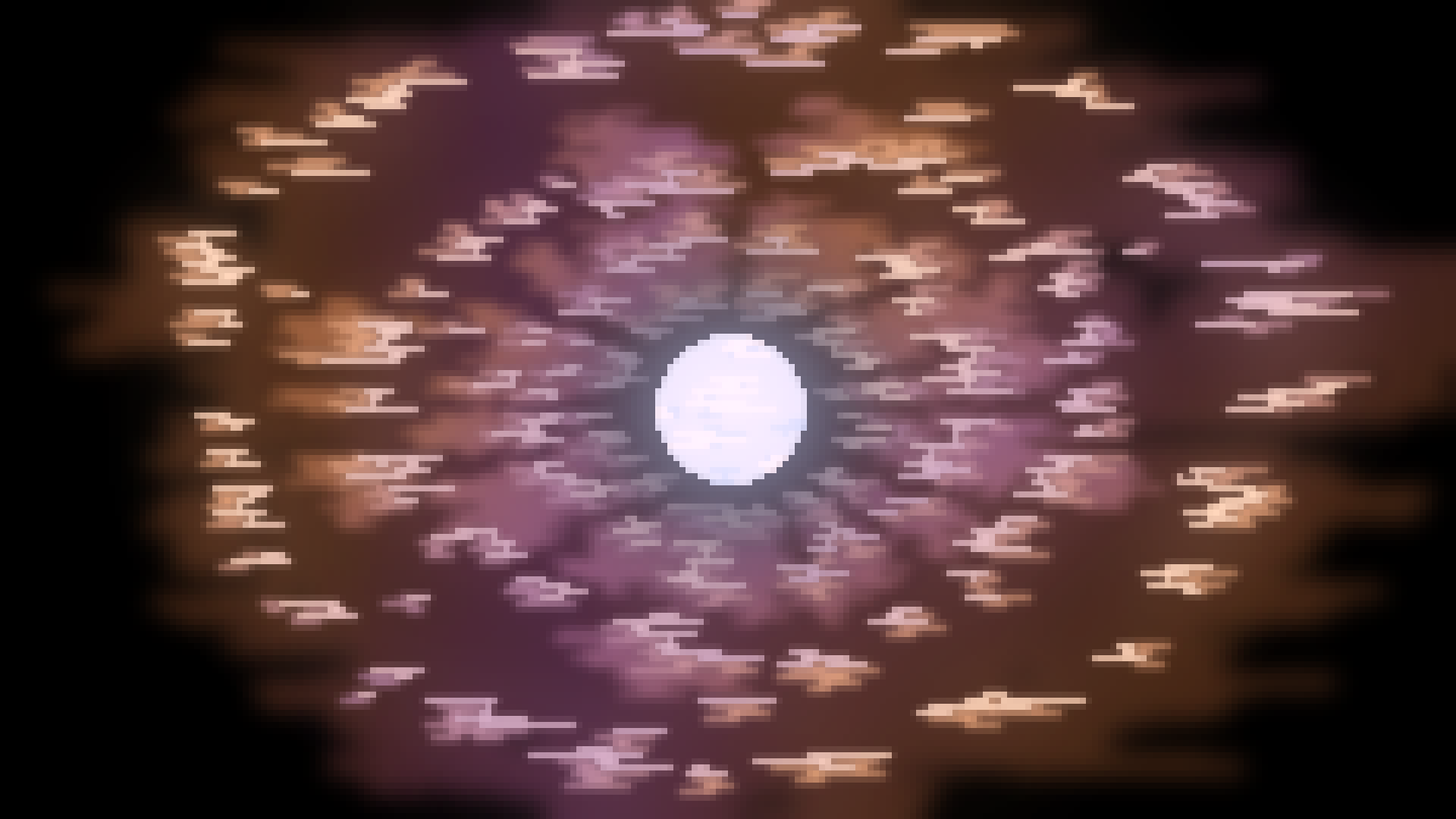

Wolf Rayet Star
Wolf Rayet Stars are stars many times more massive than the sun that are about to go supernova. They are very hot and expell a lot of their mass into the space around them.
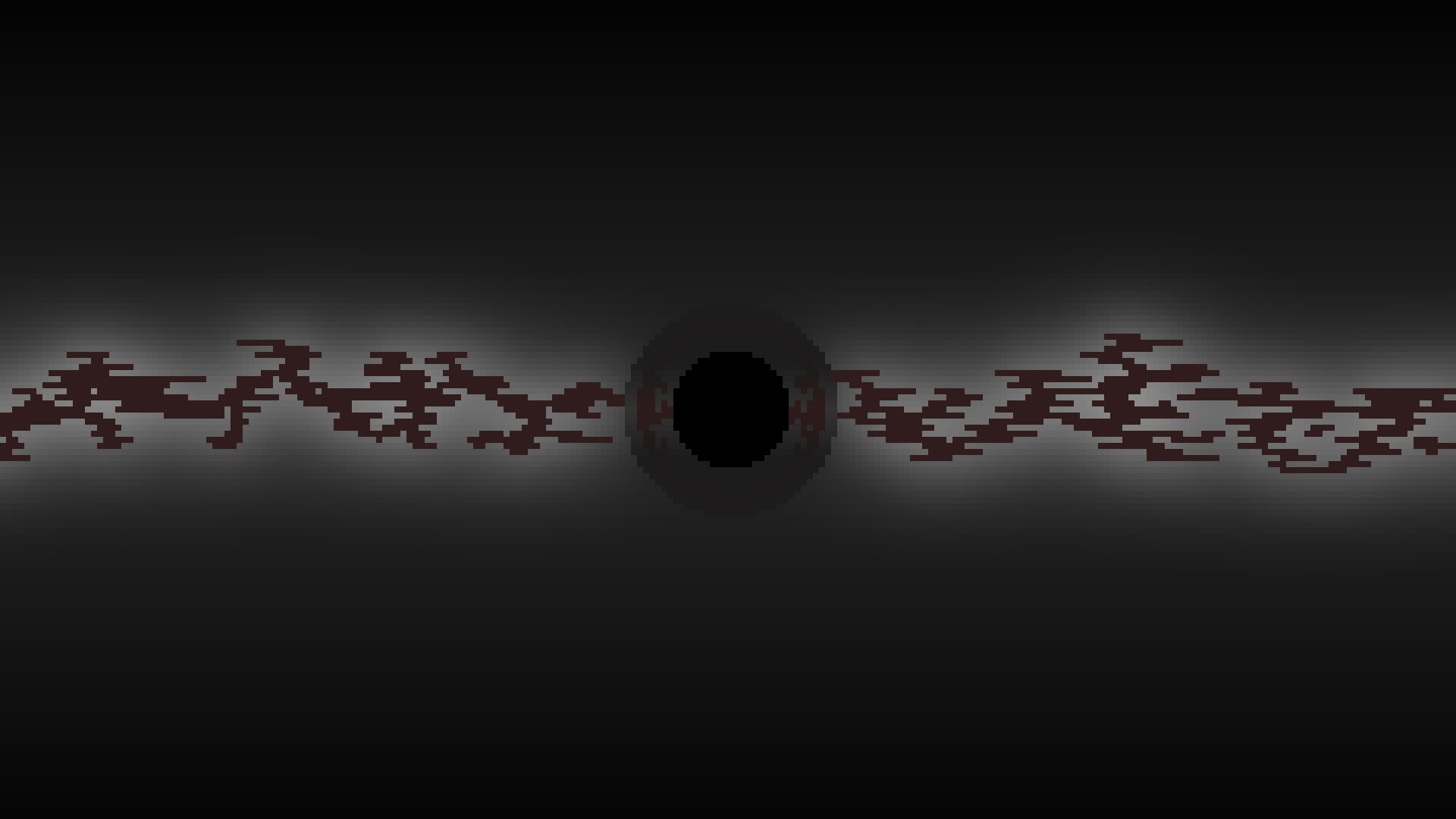
Black Hole
Black holes are formed when a star over 20 times as massive as the sun implodes. When the star colapses in on itself, there is no force strong enough to prevent a full collapse, the remnance of this process is a black hole

Supermassive
Black Hole
Black Hole
A suppermassive black hole is a black hole that formed billions of years ago. They are millions to billion times more massive than the sun and at the center of every large galaxy. A supermassive black hole that activly consumes stars and produces EXTREMLY large ammounts of light are called quasars.
Nebula
Nebulas are constentrated areas of gas and dust that form after supernovae. Nebulas are the birthplaces of many stars and look gorgeous.
Open
Cluster
Cluster
Open clusters are small groups of stars, usually containing only a few dozen of them.
Globular
Cluster
Cluster
Globular clusters are very large clusters of stars that are held together by gravity. These clusters can contain thousands upon thousands of stars inside.

Galactic
Groups
Groups
Galactic groups are groups of galaxys. Our local galactic group consists of our galaxy (milky way) and the Andromeda galaxy.
Super
Clusters
Clusters
Super clusters are clusters of galaxies, consisting of thousands of galactic groups.

Voids
Voids are areas of the universe where there are very few galaxies. When the universe was very small there were regions with less mass than other regions. Then,h when the universe expanded it resulted in massive voids seperating super cluseters.
Universe
The universe is everything. All stars, galaxies, clusters, and voids make up the universe. We can only see a small portion of the universe because light from the distant edges takes so long to reach us.

Quazi-Stars
A quazi-star is a theoretical star that could have formed in the early universe. Theory states that these stars were so massive that once they went supernova, the blast didn't even leave the star, making the black hole leftover eat the star from the inside out.
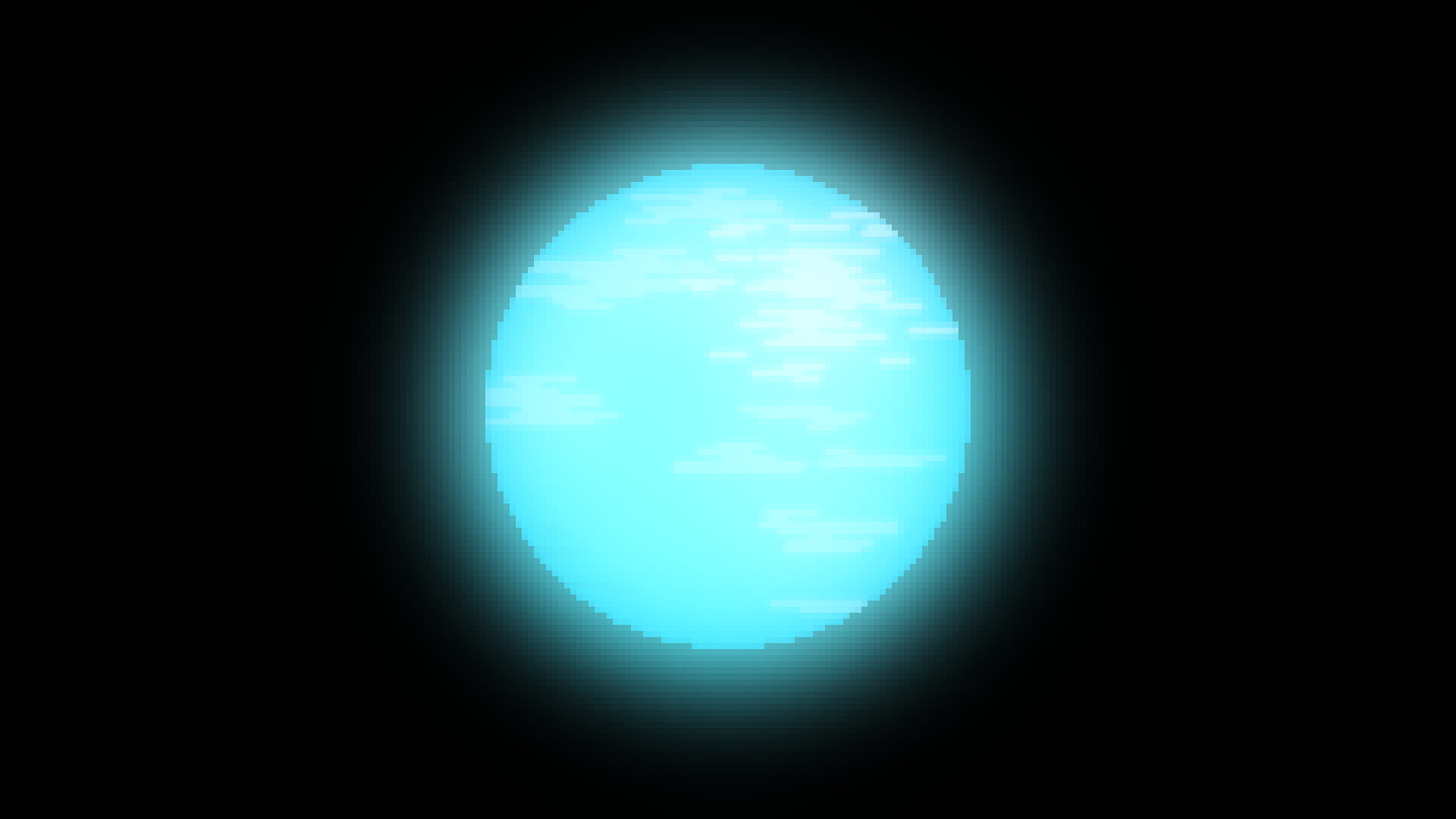

Strange Star
Strange stars, or quark stars, are theoretical objects that consist of only strange quarks. It is thought that some neutron stars are so dense that they warp matter into strange matter. A type of matter we don't know much about yet.
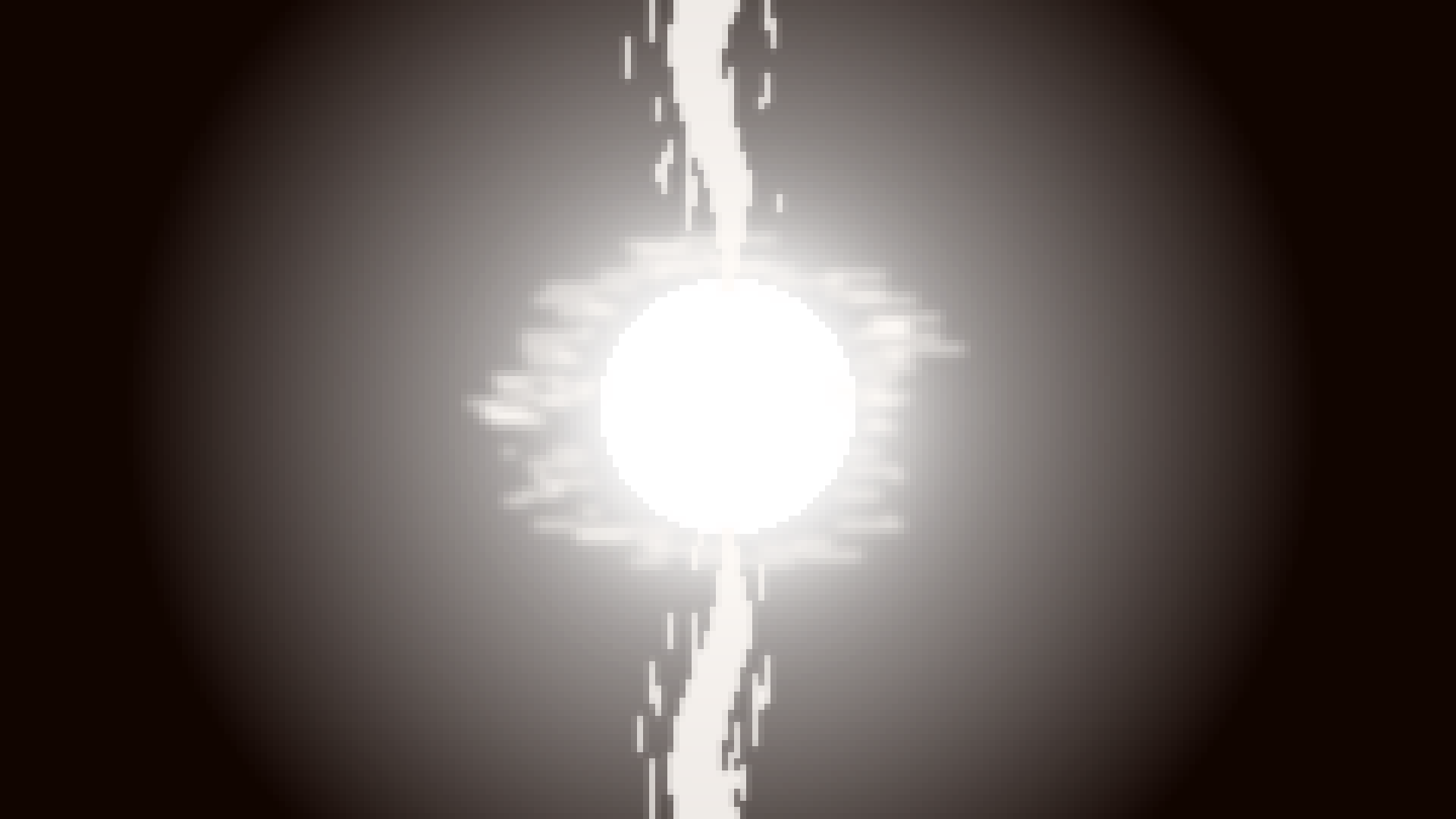

White Hole
A white hole is a theoretical opposite to a black hole. In theory, nothing can enter a white hole (as opposed to nothing exiting a black hole). And whatever enters a black hole will leave a corresponding white hole after an infinite ammount of time.
-Events-
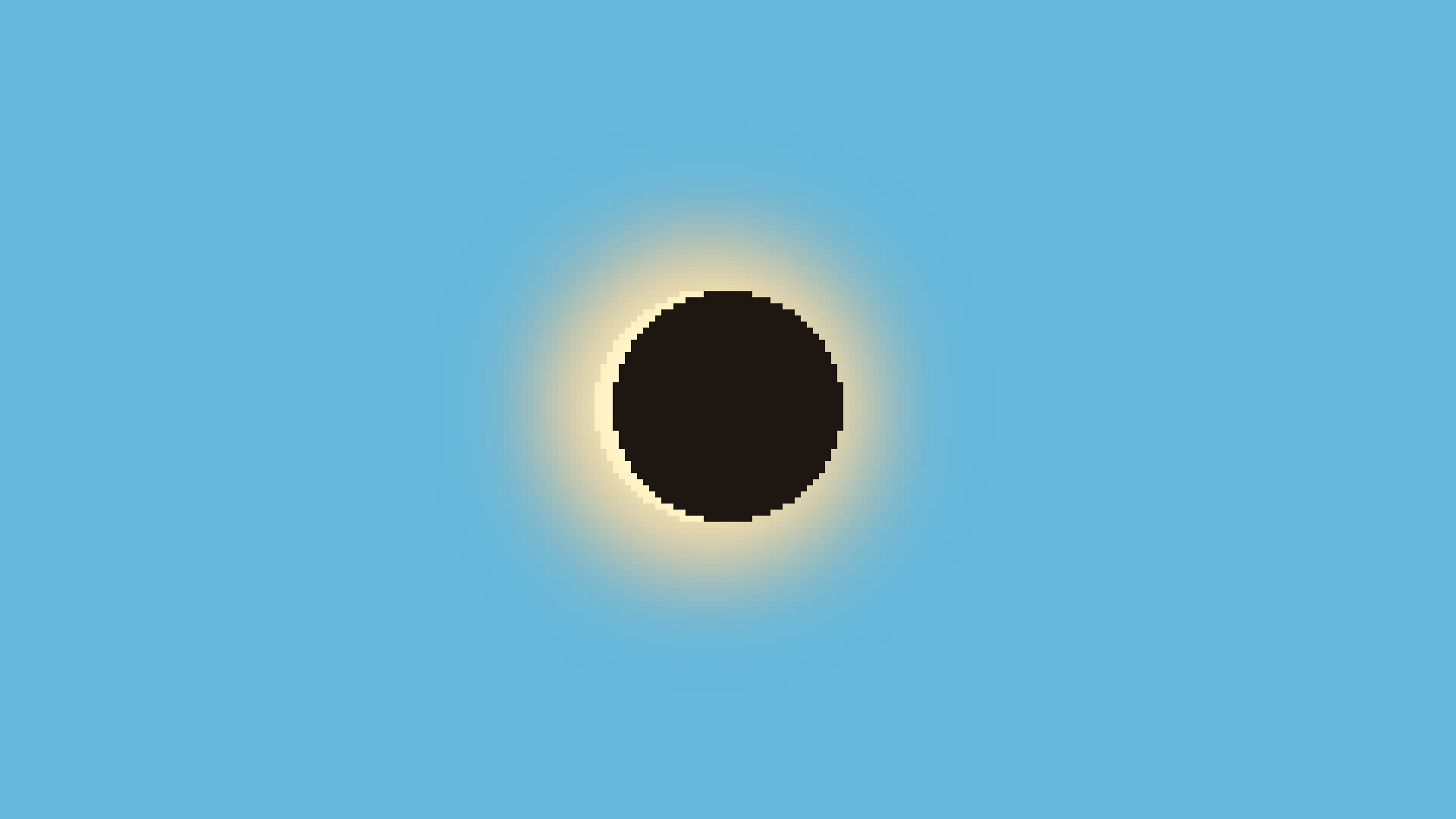
Eclipse
An eclipse occurs when an astronomical body goes infront or behined of another. Usually occuring with a star, plannet, and moon.
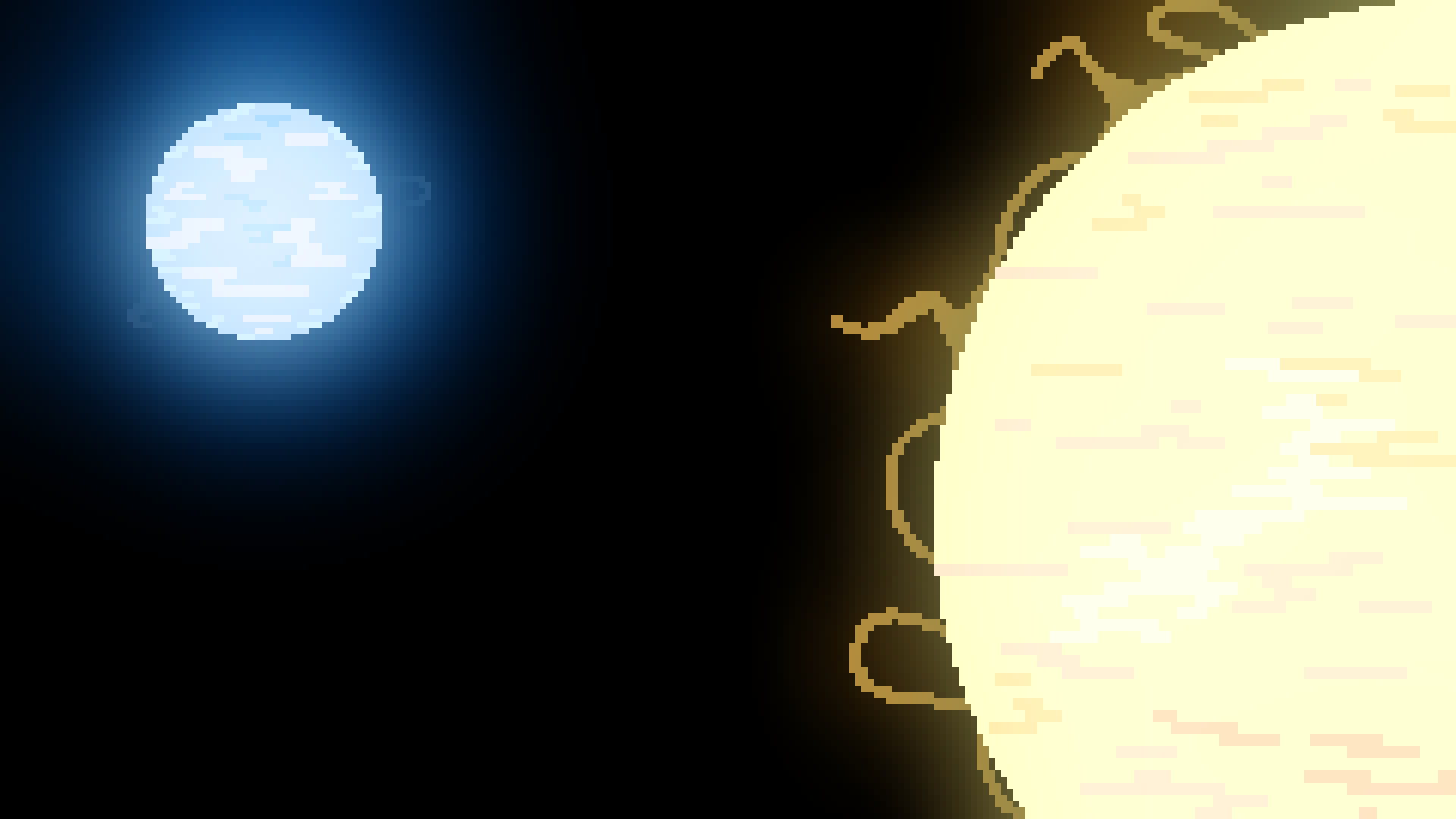

Binary
System
System
Sometimes a solar system can have multiple stars that are gravitationally bound to one another. A binary system has 2 stars, however systems can have even more. Planets can orbit a single star that orbits with another star, or a planet can orbit multiple stars depending how far the stars are from one another.
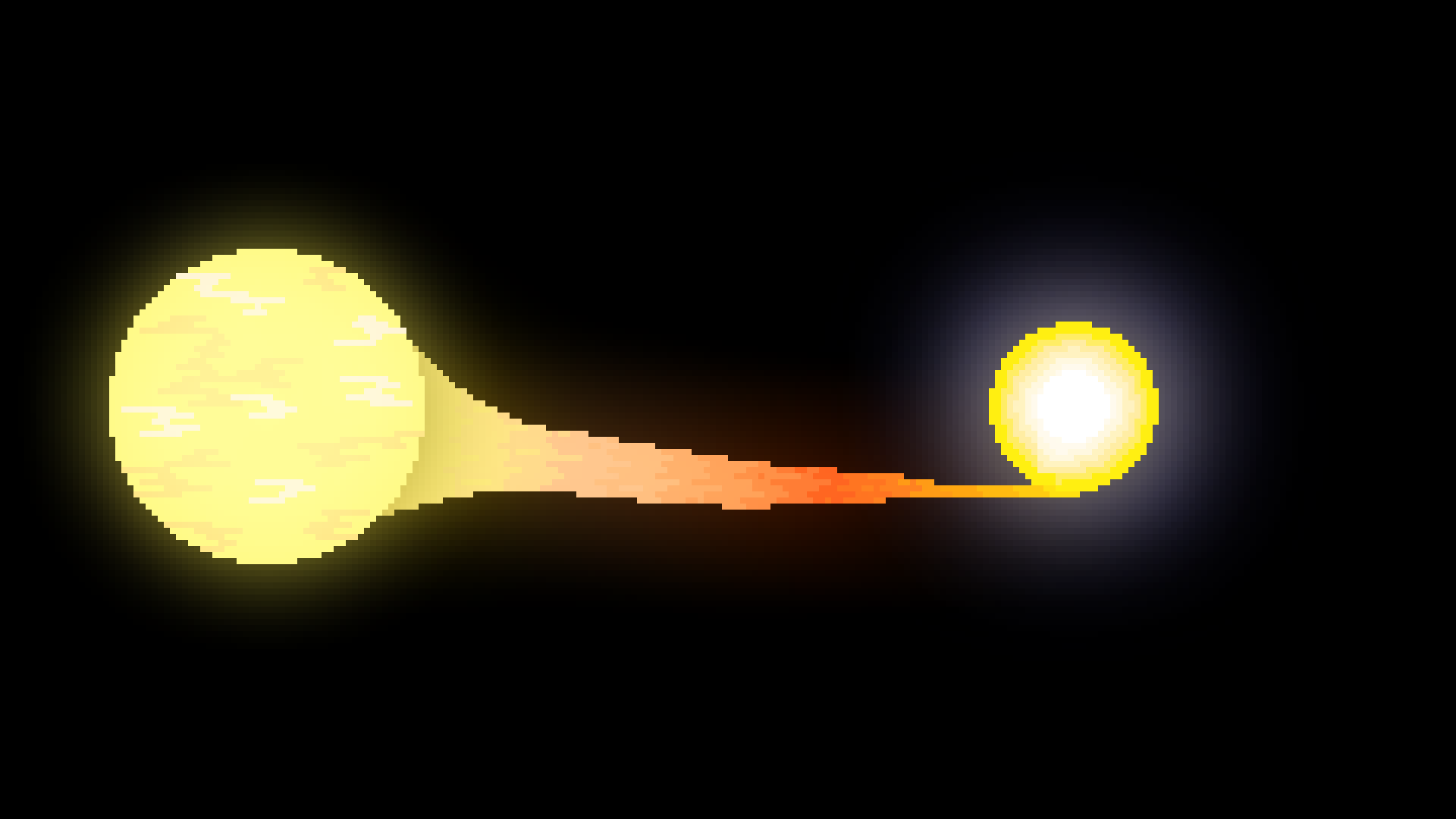
Nova
When there is a binary system with a white dwarph, sometimes the dwarph star will consume its counterpart and occationally explode the matter gathered from the star back into space.
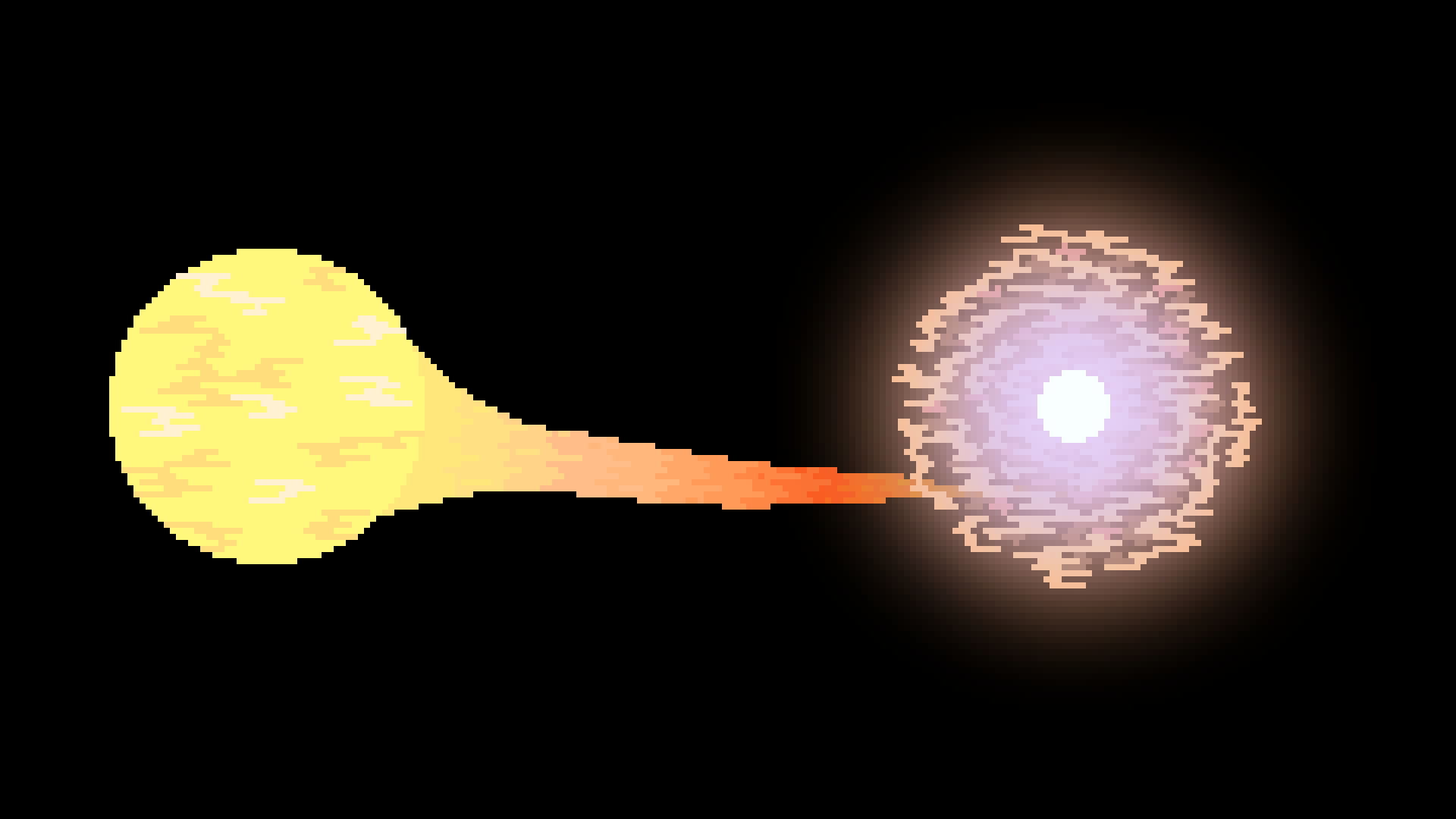
Type 1
Supernova
Supernova
When the procces that causes a nova builds up to an exteme ammount, it can trigger a massive explosion, destroying the white dwarph star.
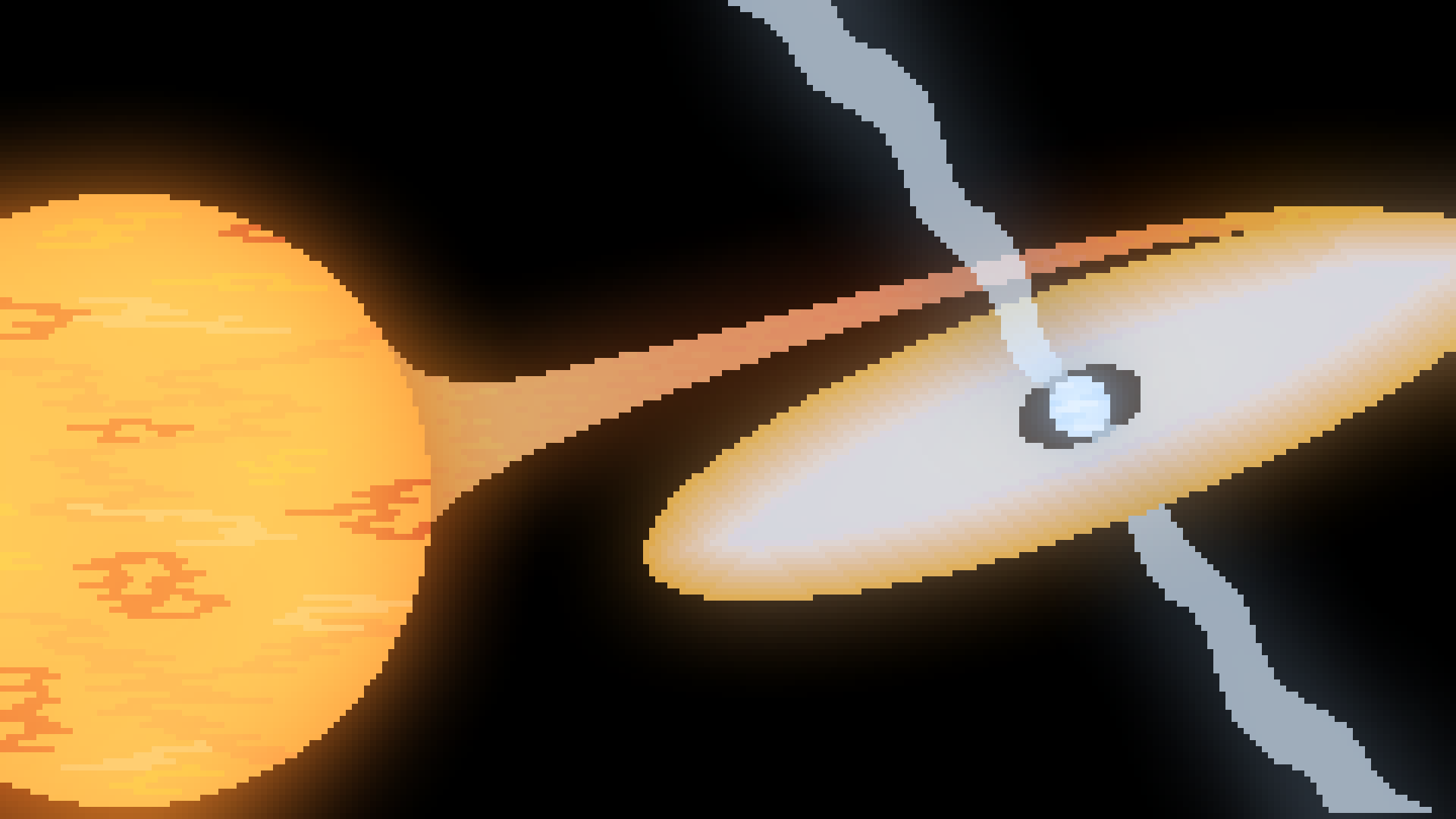
X-Ray
Burster
Burster
Very similar to a nova, X-Ray Bursters happen when a star is being consumed by a neutron star instead of a white dwarph. The neutron star ejects its mass a lot more, and much more frequently than a white dwarph, so it appears brighter.
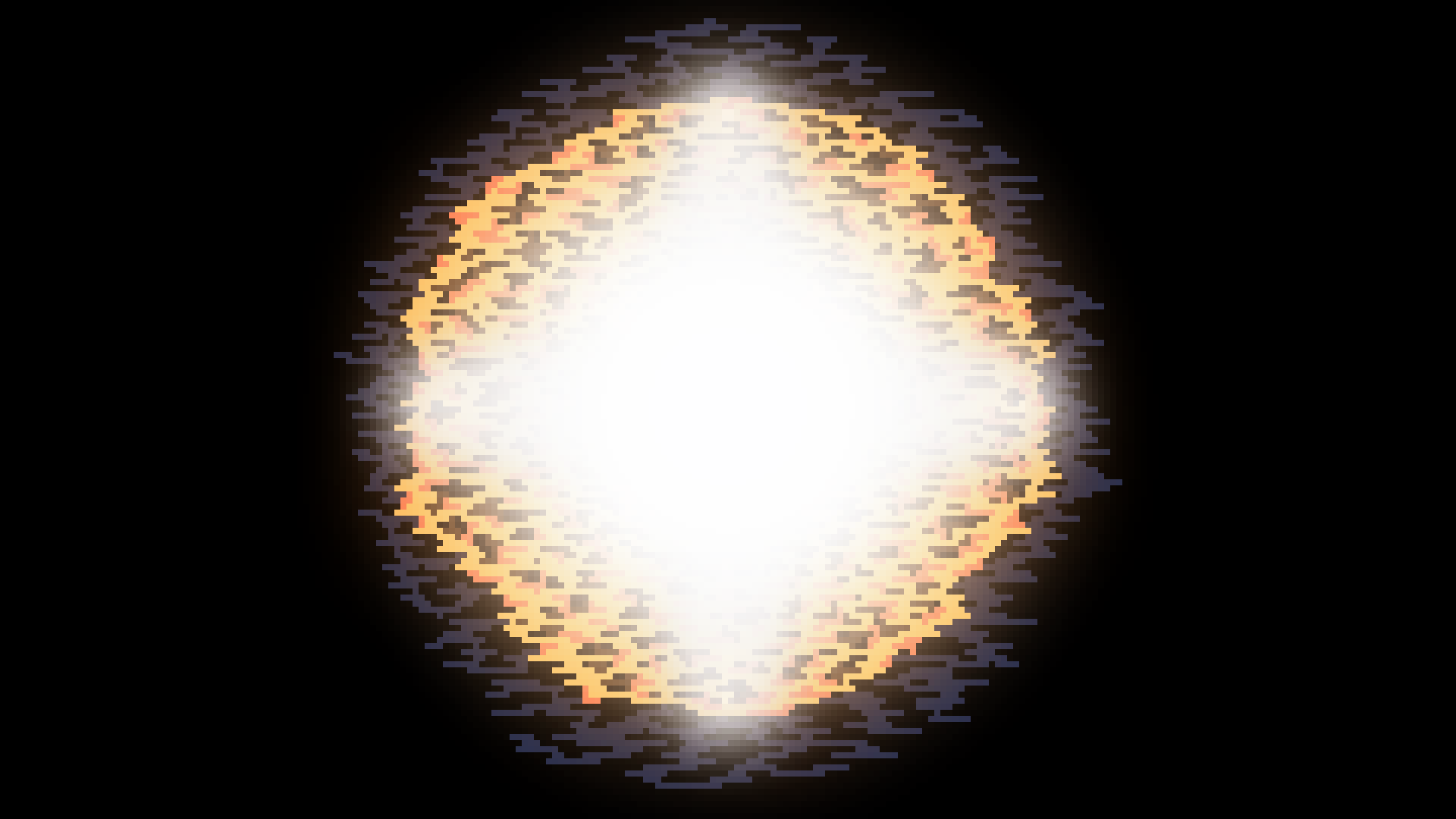
Type 2
Supernova
Supernova
A type 2 supernova occurs at the end of a high mass star's life. When the star runs out of matter to fuse and has nothing to combat the force of gravity. The star collapses in on itself and a shockwave is sent from its iron core, this shockwave expells the entire star at a fraction of the speed of light in an enormous explosion.
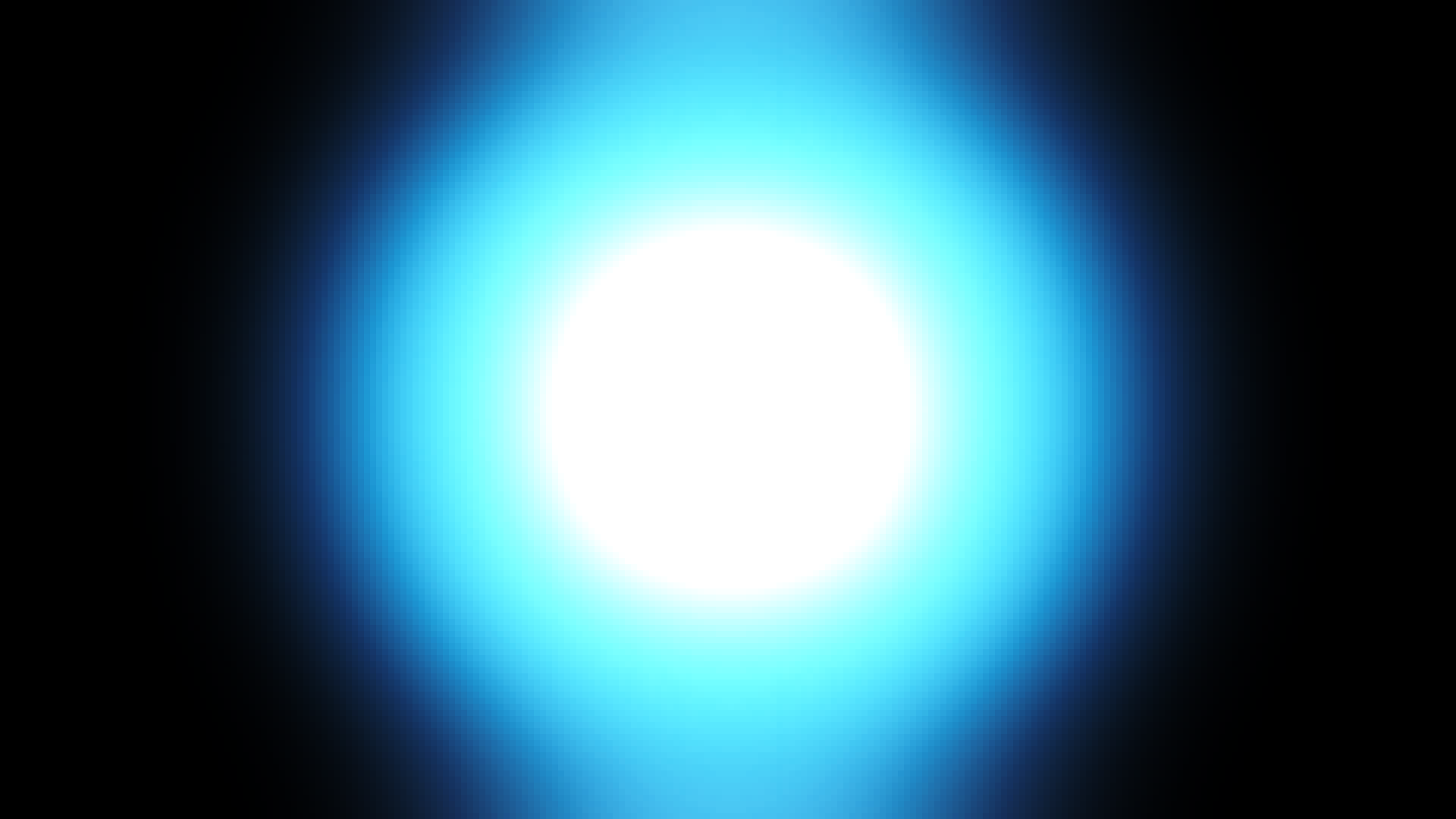

Big Bang
The Big Bang is what started the universe. It is believed that the universe started as a single point and expanded.
-Parts-
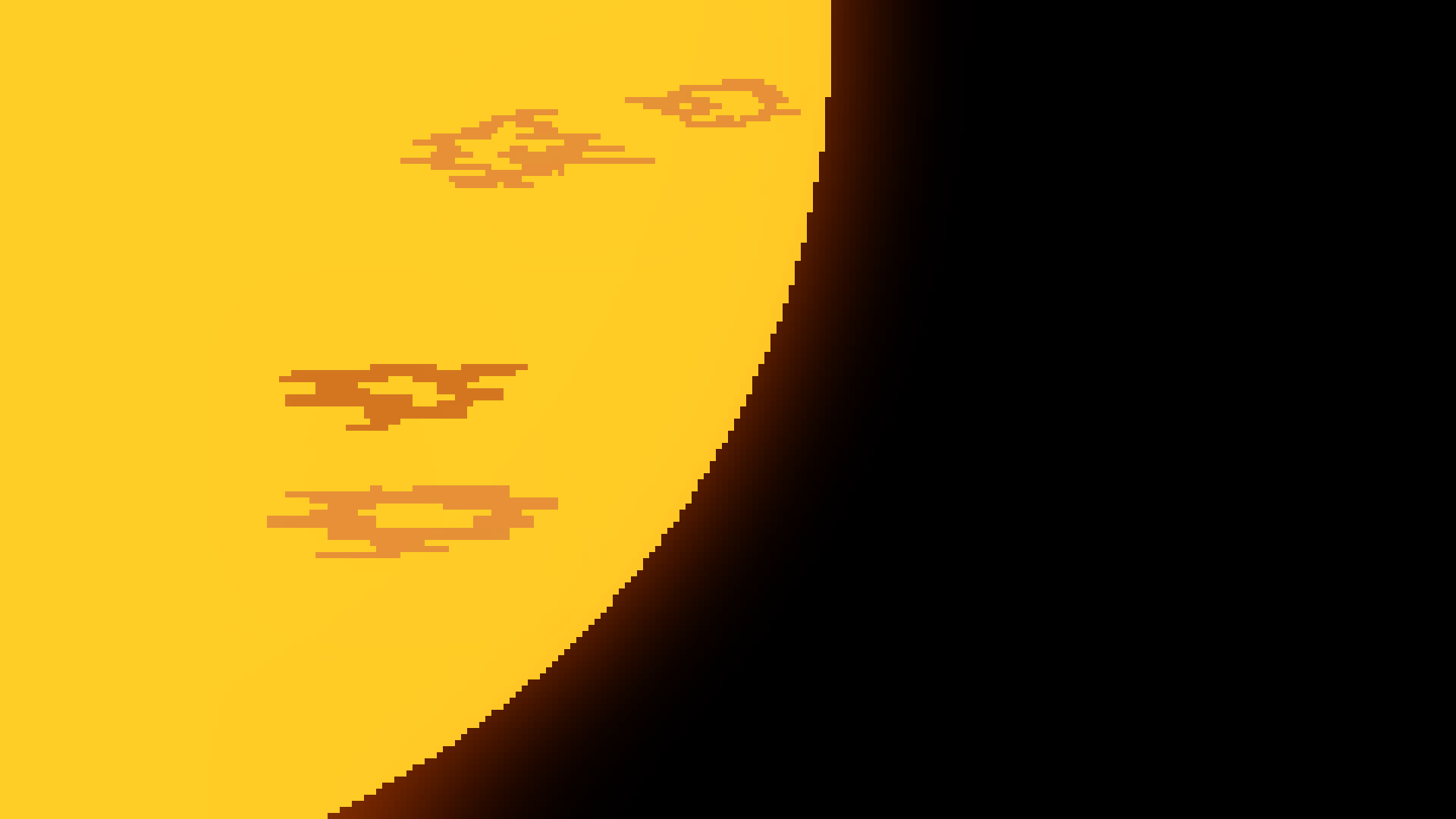

Sunspots
{Star}
{Star}
Sunspots are cool (still hot) spots on the sun and are caused by disturbances in the stars magnetic sphere. They act as a gateway for promenences and solar flares.

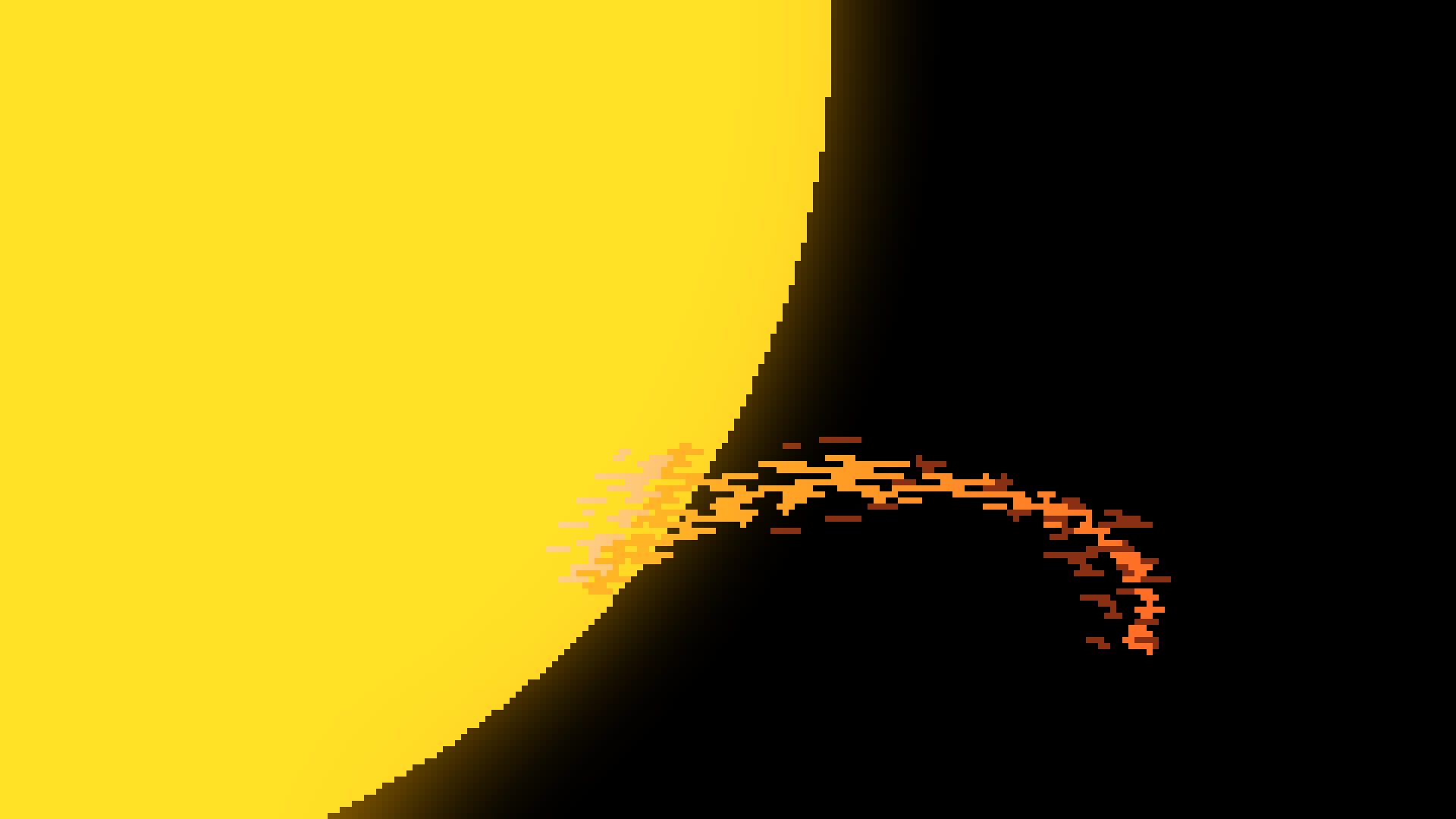
Promenences
{Star}
{Star}
Promenences happen when matter from the sun is launched away from the surface and arches back. These prominences are enormous and some can fit multiple Earths inside.
Solar Flare
{Star}
{Star}
Solar flares are like promoneces except they don't go back to the stars surface, instead they get expelled into space and can cause damage to human technology if they hit Earth.
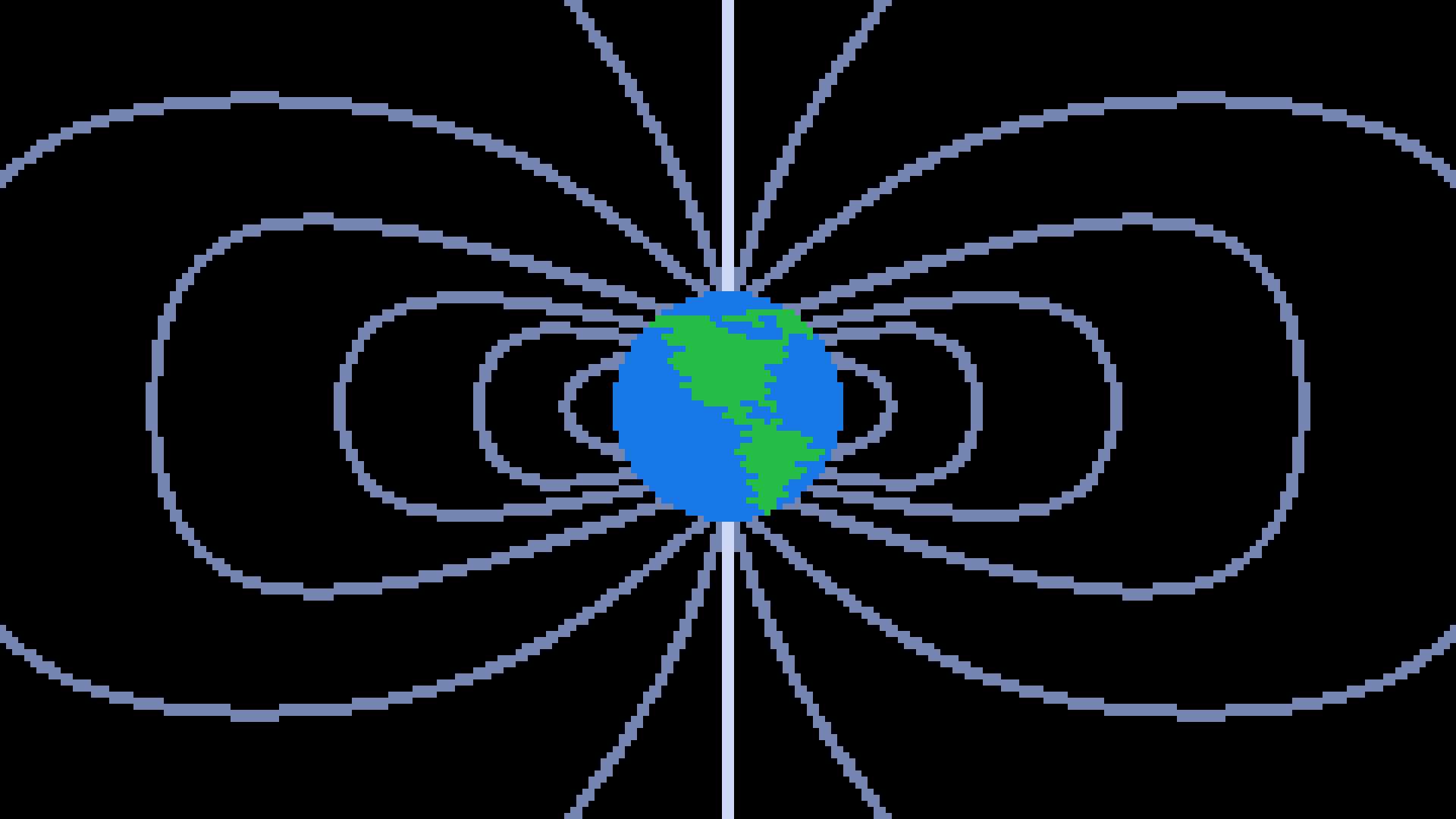
Magnetic
Field
Field
Magnetic fields are apart of most large bodies. They are extremly active in gas giants, stars, neutron stars, and black holes. Magnetic fields can also protect planets from solar wind and flares.

Event
Horison
{Black Hole}
Horison
{Black Hole}
An Event horisons is the point where the escape velocity equals the speed of light, meaning that even light cannot escape the gravitational pull of a black hole past this point.

Singularity
{Black Hole}
{Black Hole}
The singularity is the incredibly dence point at the center of a black hole. Since when a black hole collapses, there is no force strong enough to stop the core from collapse infinitly, it is thought all of the matter piles onto this single point.

Accretion
Disk
Disk
An accretion disk is disk of matter that accrets around a dence object, like a black hole, white dwarph, or neutron star. Matter gets heated to extreme tempratures as it gets closer to the body. The accretion disks of quasars are what give them their luminocity.

Jets
A jet is radiation that gets ejected from a super dence object such as a pulsar or a black hole.

Core
{Galaxy}
{Galaxy}
The galactic core is the center of a galaxy, it has a high population of stars and contains mainly older stars.

Disk
{Galaxy}
{Galaxy}
The galactic disk is the part of a spiral galaxy that has the majority of the gas and dust. It usually has younger and less stars than the galactic core.

Halo
{Galaxy}
{Galaxy}
The galactic halo is the part of a spiral galaxy where stars are not in the disk but are still gravitationally bound to the galaxy. There are much fewer stars in the halo than in the disk or the core. Most stars are older.
-Science-

Constellation
A constellation is a group of stars that resemble an image of something. Ancient astronomers named these clusters of stars.

Astronomical
Unit
Unit
An astronomical unit is the distance between the earth and the sun (on average). It is usually used to show distances in a solar system.

Light Year
A light year is the distance light can travel in a year. It is usually used to show distances between stars or galaxies. A parsec is also a unit of measurement that is 3.26 light years long.

HR Diagram
The HR diagram is a chart categorizing where stars are in temprature, brightness, and size. The HR diagram points out a pattern in stars and predicts what will happen to them later in their lives.
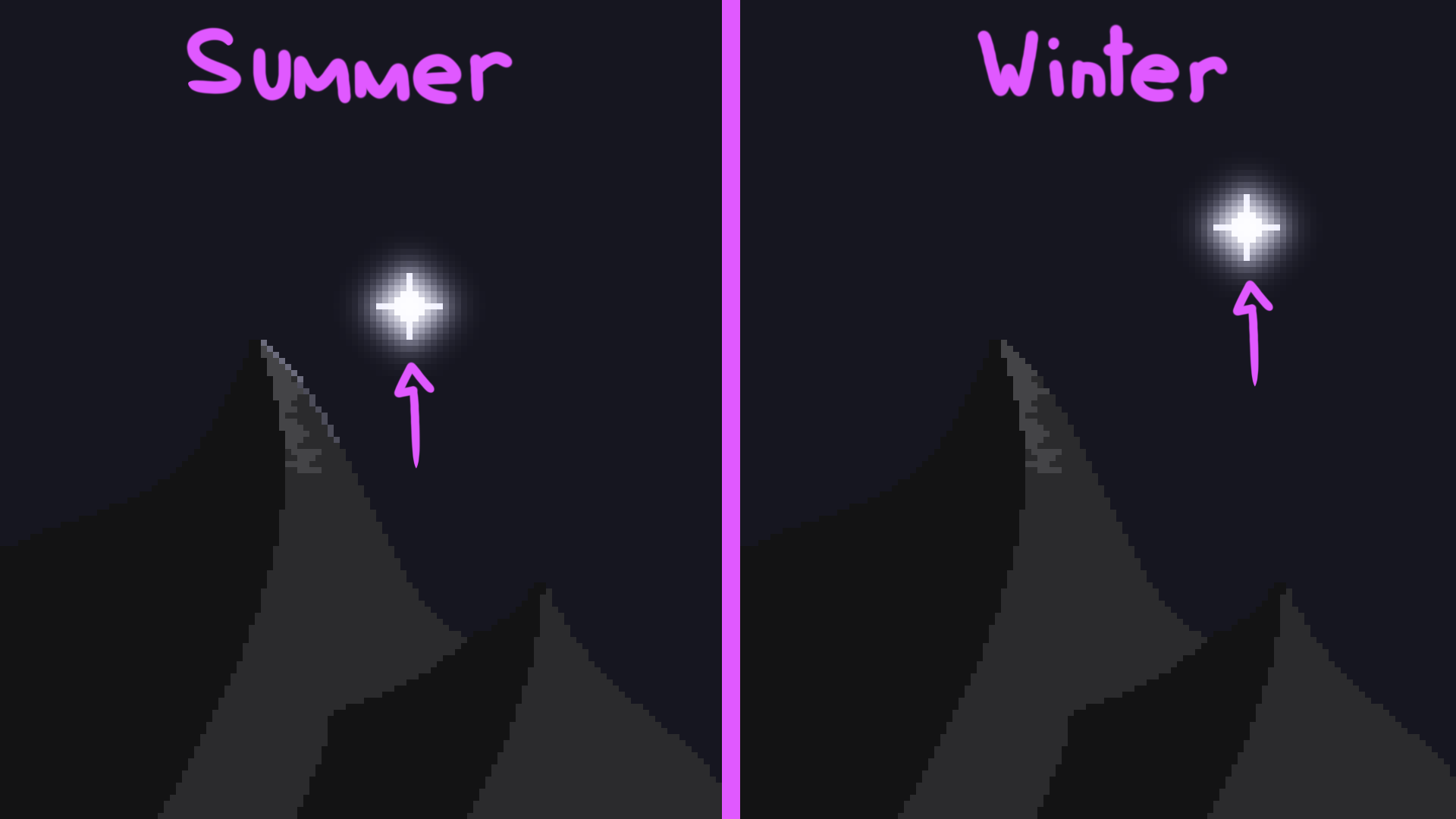

Parallactic
Shift
Shift
The parallactic shift is the angle made when observing a star in one time of year compared to the opposite time of year. The star will appear in a different position in the sky because the Earth is in a different place at different times of the year. This can be used to get distances between stars.
Goldilocks
Zone
Zone
The goldilocks zone is an invisible zone inbetween where water frezes and evaporates. Each star has a different goldilocks zone depending on its size and temperature. If a planet fall inside the goldilocks zone then it could possibly harbor life.

Satellite
A satelite is something sent up into orbit by humans. A "natural satellite" refers to a moon but we generally refer to satellites as man made machines, usually sent up to collect data, send signals, or observe the far reaches of the cosmos.
-Classifications-

Terestrial
{Planet}
{Planet}
A terrestrial planet is rocky (like the earth). They usually have no rings, few moons, low mass and size, and a high density.
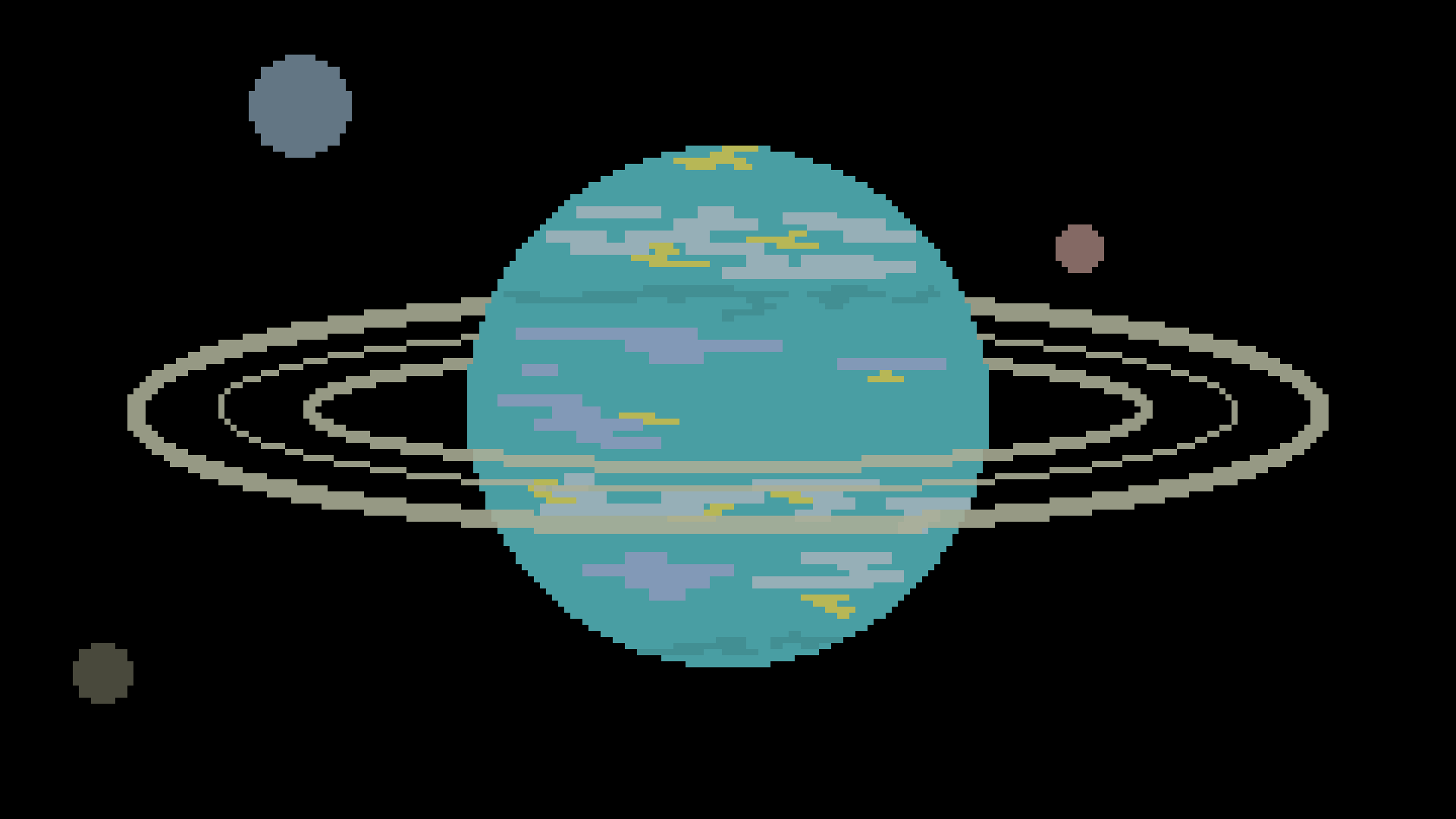
Jovian
{Planet}
{Planet}
Jovian planets, also known as gas giants, are very big and gasseous. They usually have rings, a lot of moons, high mass and size, and a low density.

Dwarf
{Planet}
{Planet}
A dwarph plannet is a celestial body in between an asteroid and a plannet in size. Dwarf plannets are normally the size of large moons but not large enough to be fully fleged planets. They are also lighter and formed differently than regular planets.
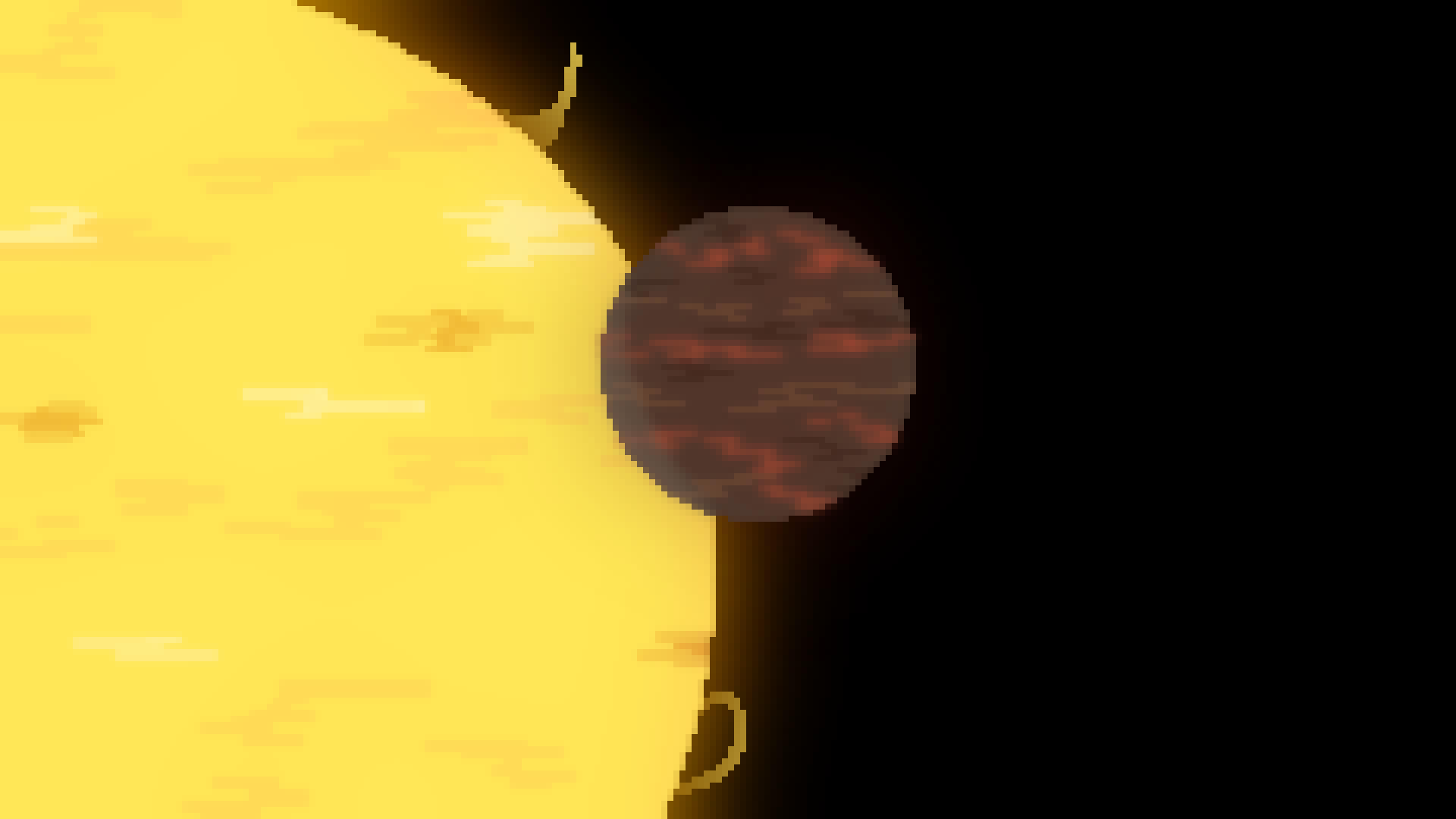

Hot Jupiter
{Planet}
{Planet}
A hot jupiter is a gas giant nearly 10 times more massive than jupiter. These planets orbit their stars very closely and can even wobble the star they orbit due to their large size and close proximity.

Ice Giant
{Galaxy}
{Galaxy}
Ice giants are like gas giants but extremely cold. Most ice giants are made up of mostly methane. Uranus and Neptune are ice giants.

Rogue
{Planet}
{Planet}
An rogue planet is a planet that was ejected from it's solar system. These lone planets roam the cosmos alone and in darkness. This is not to be confused with 'exoplanet', which is any planet located outside of OUR solar system
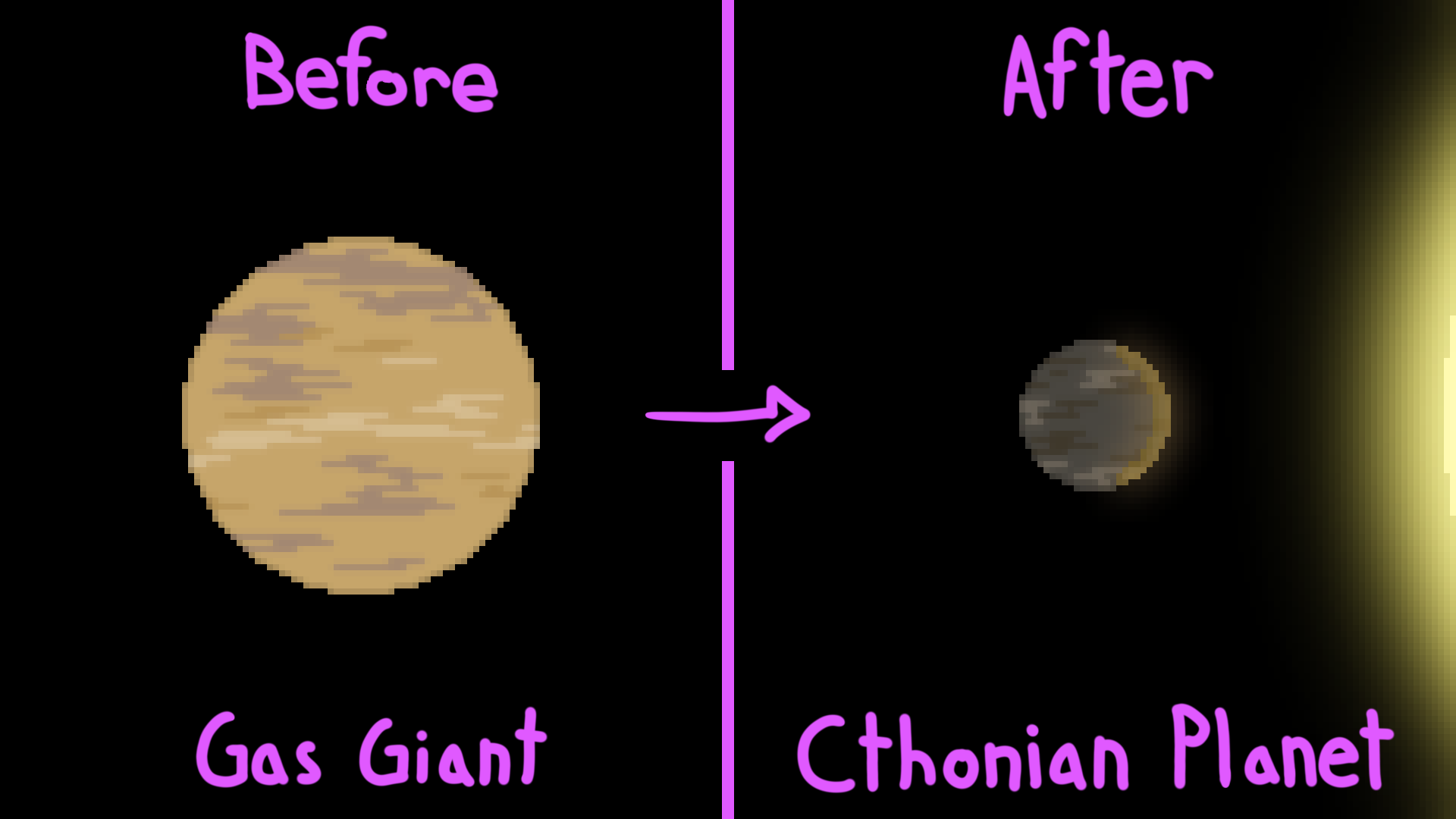
Cthonian
{Planet}
{Planet}
A cthonian planet is a former gas giant, that was stripped of it's outer gaseous lairs and left with only a solid core. These resemble terestrial planets in their current form.

Water World
{Planet}
{Planet}
A water world is a planet that is completely submerged in a thick layer of water. These worlds usually have much more water than earth does.
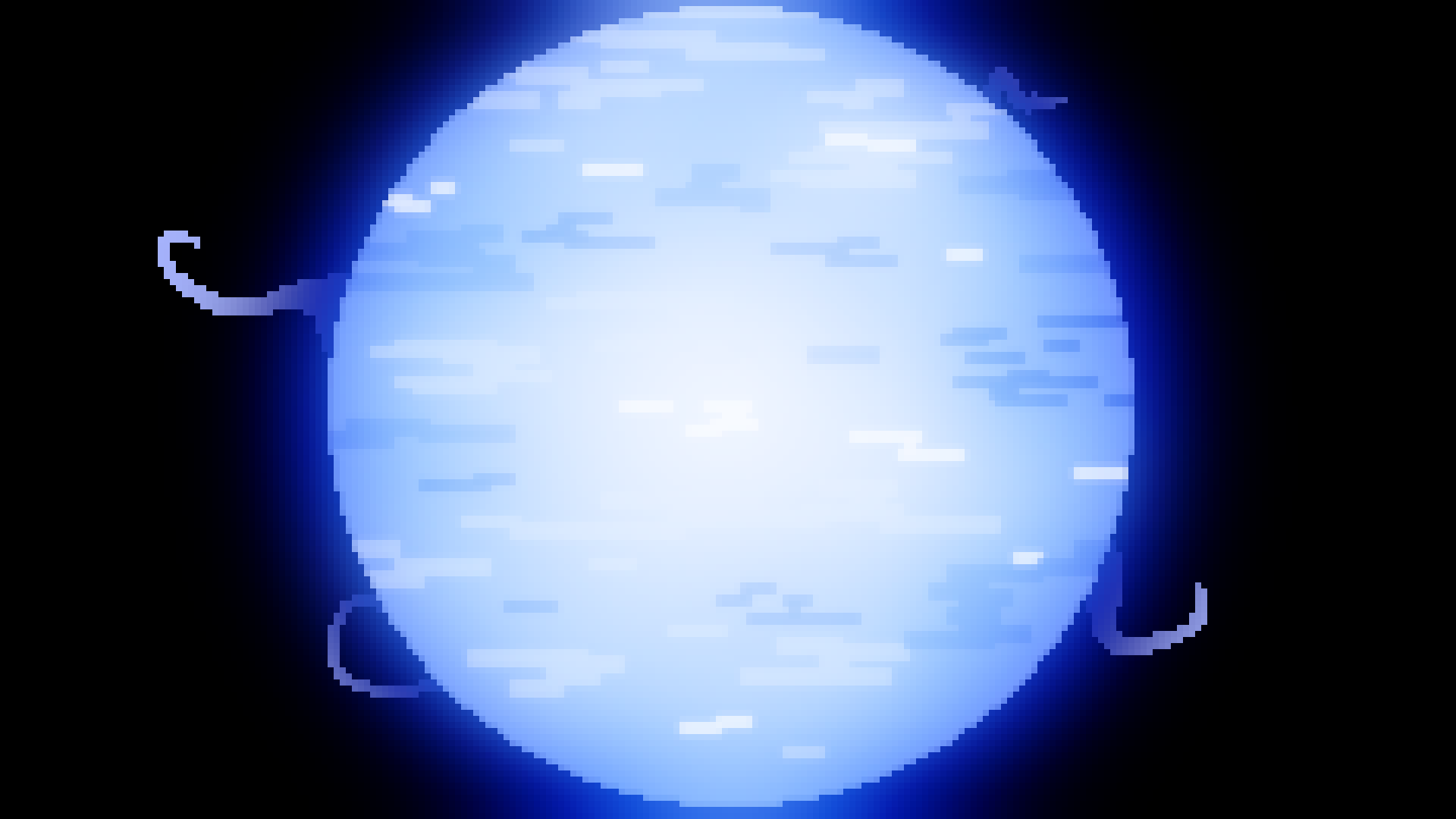

O type
{Star}
{Star}
Blue Star
30,000*K+
40,000+ Solar luminocity
15+ Solar masses
7+ Solar radii
10 million - 50 million year lifespan
0.00005% of all stars
30,000*K+
40,000+ Solar luminocity
15+ Solar masses
7+ Solar radii
10 million - 50 million year lifespan
0.00005% of all stars
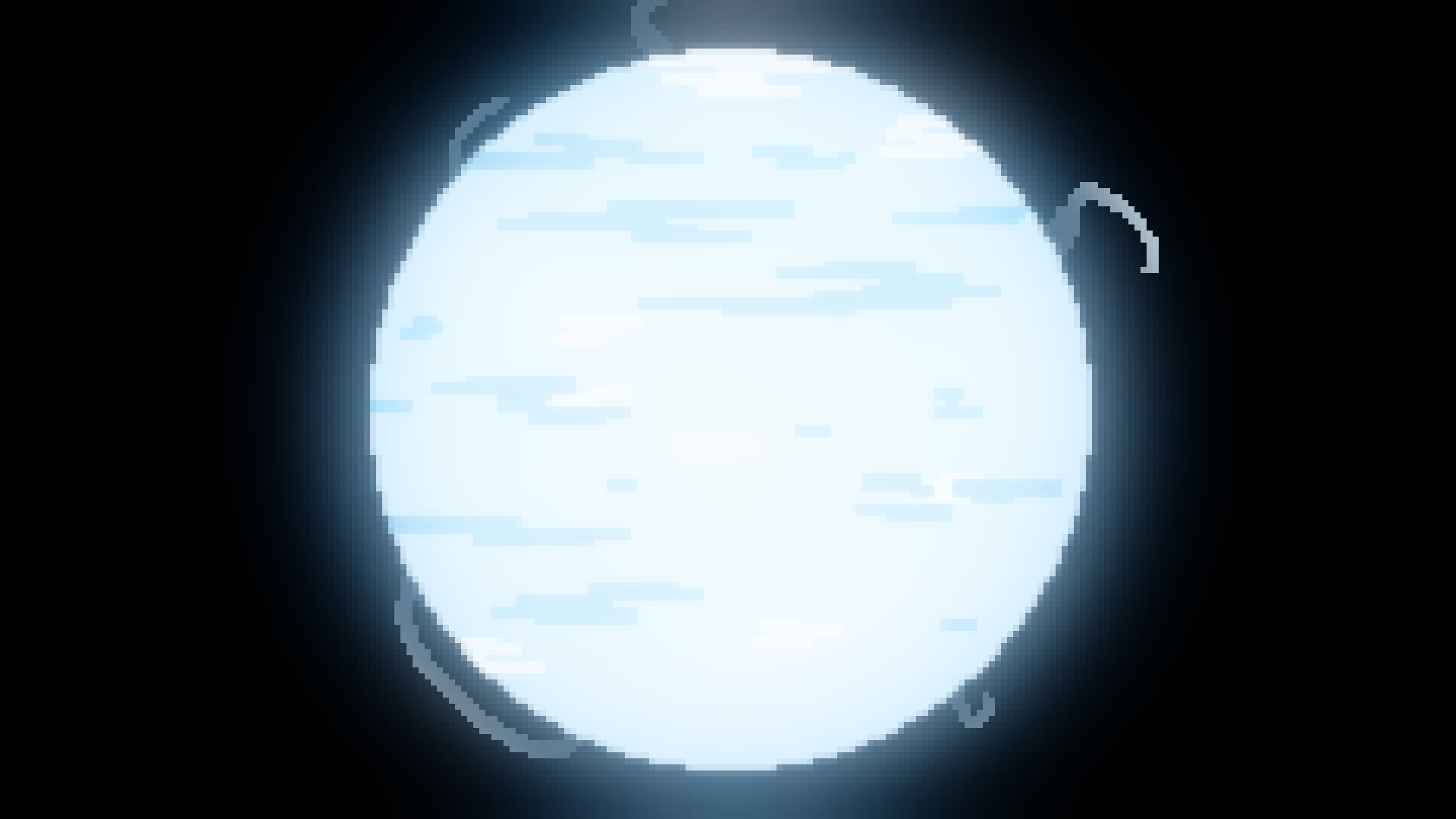

B type
{Star}
{Star}
Blue-White Star
10,000*K - 30,000*K
25-30,000 solar luminocity
2-16 Solar masses
2-7 Solar radii
50 million - 100 million year lifespan
0.13% of all stars
10,000*K - 30,000*K
25-30,000 solar luminocity
2-16 Solar masses
2-7 Solar radii
50 million - 100 million year lifespan
0.13% of all stars
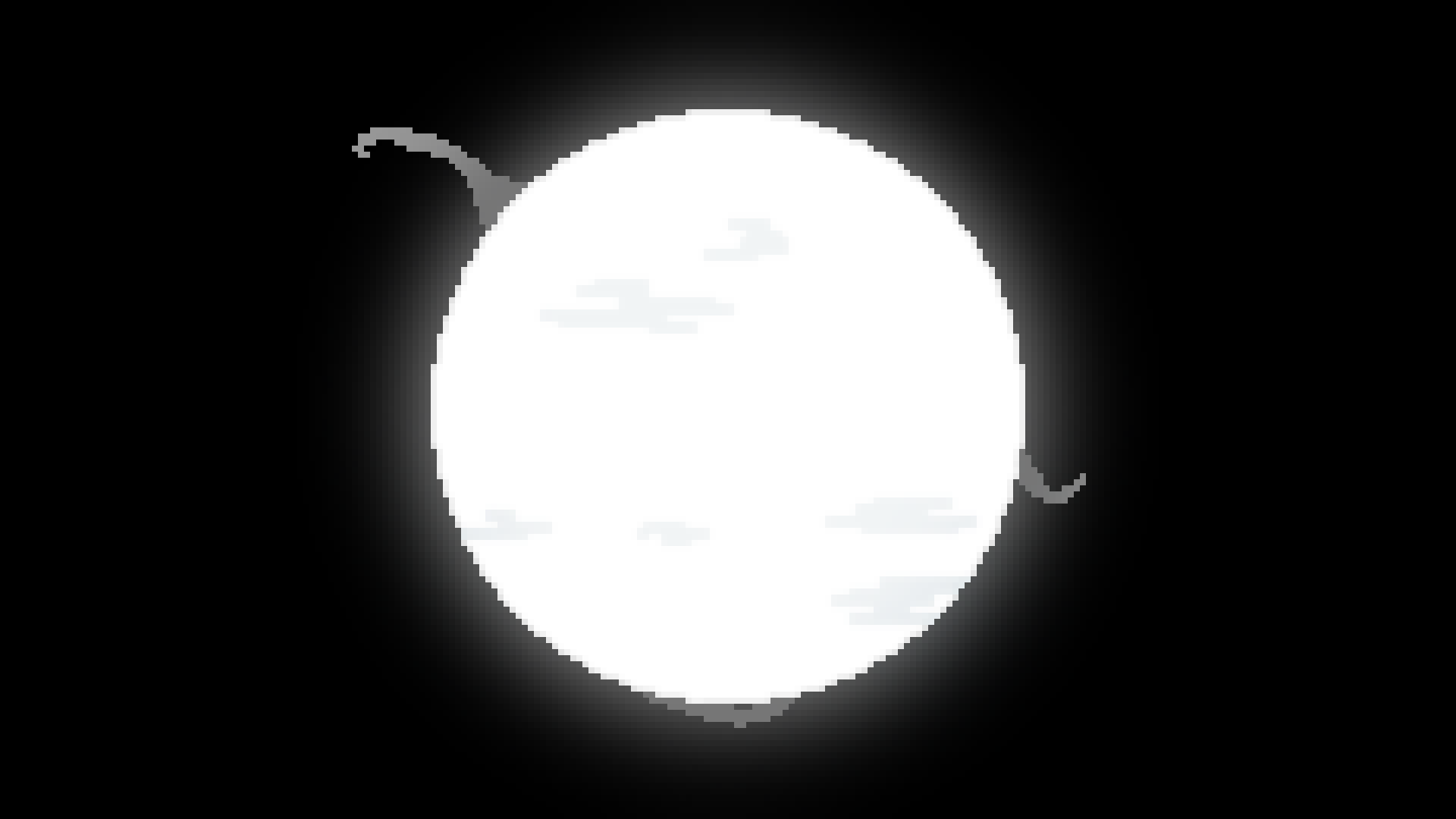

A type
{Star}
{Star}
White Star
7,500*K - 10,000*K
5-25 solar luminocity
1.4-2 Solar masses
1.4-2 Solar radii
100 million - 2 billion year lifespan
0.625% of all stars
7,500*K - 10,000*K
5-25 solar luminocity
1.4-2 Solar masses
1.4-2 Solar radii
100 million - 2 billion year lifespan
0.625% of all stars
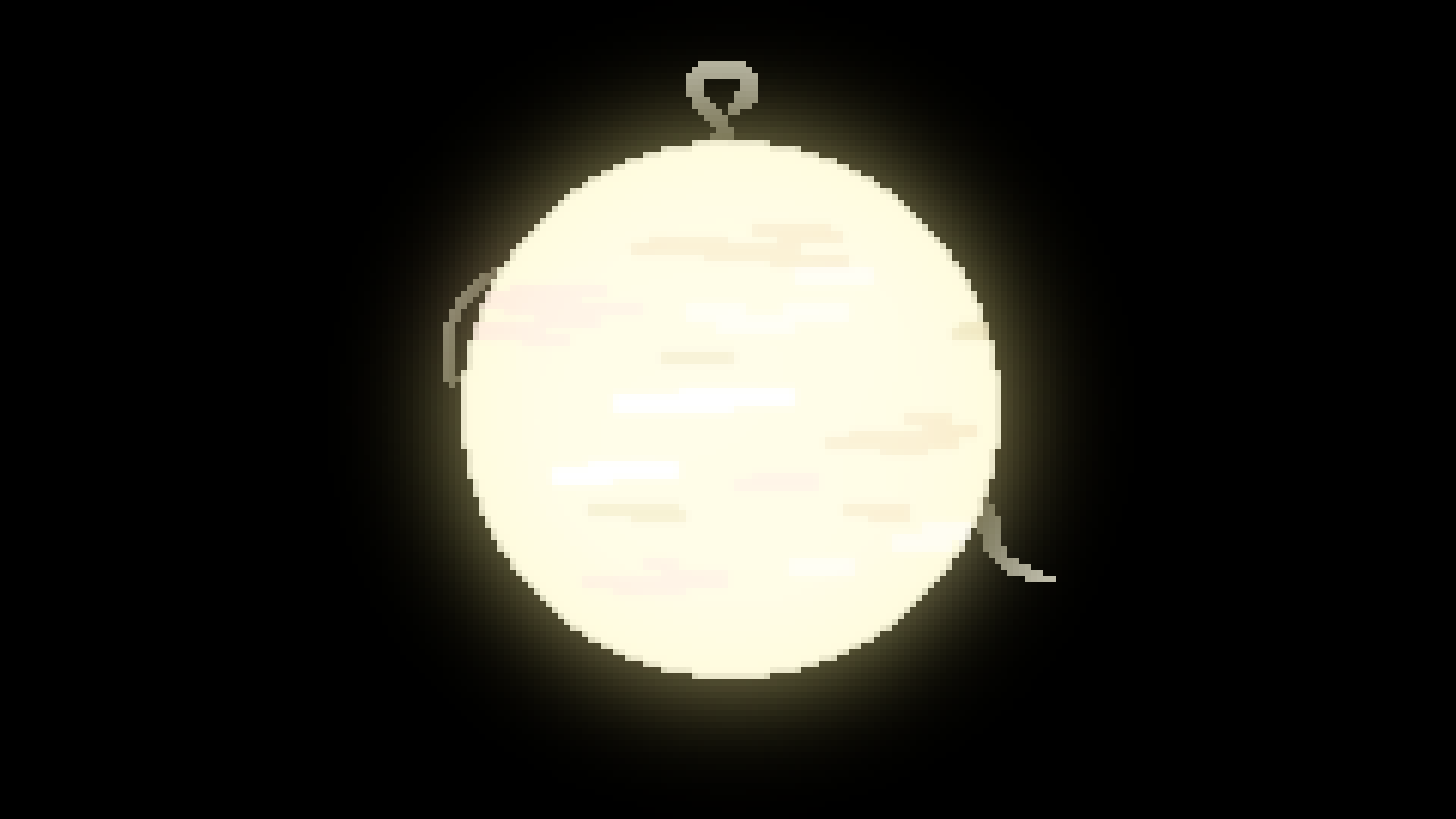

F type
{Star}
{Star}
White-Yellow Star
7,000*K - 10,000*K
1.5-5 solar luminocity
1.04-1.4 Solar masses
1.15-1.4 Solar radii
2 billion - 4 billion year lifespan
3% of all stars
7,000*K - 10,000*K
1.5-5 solar luminocity
1.04-1.4 Solar masses
1.15-1.4 Solar radii
2 billion - 4 billion year lifespan
3% of all stars
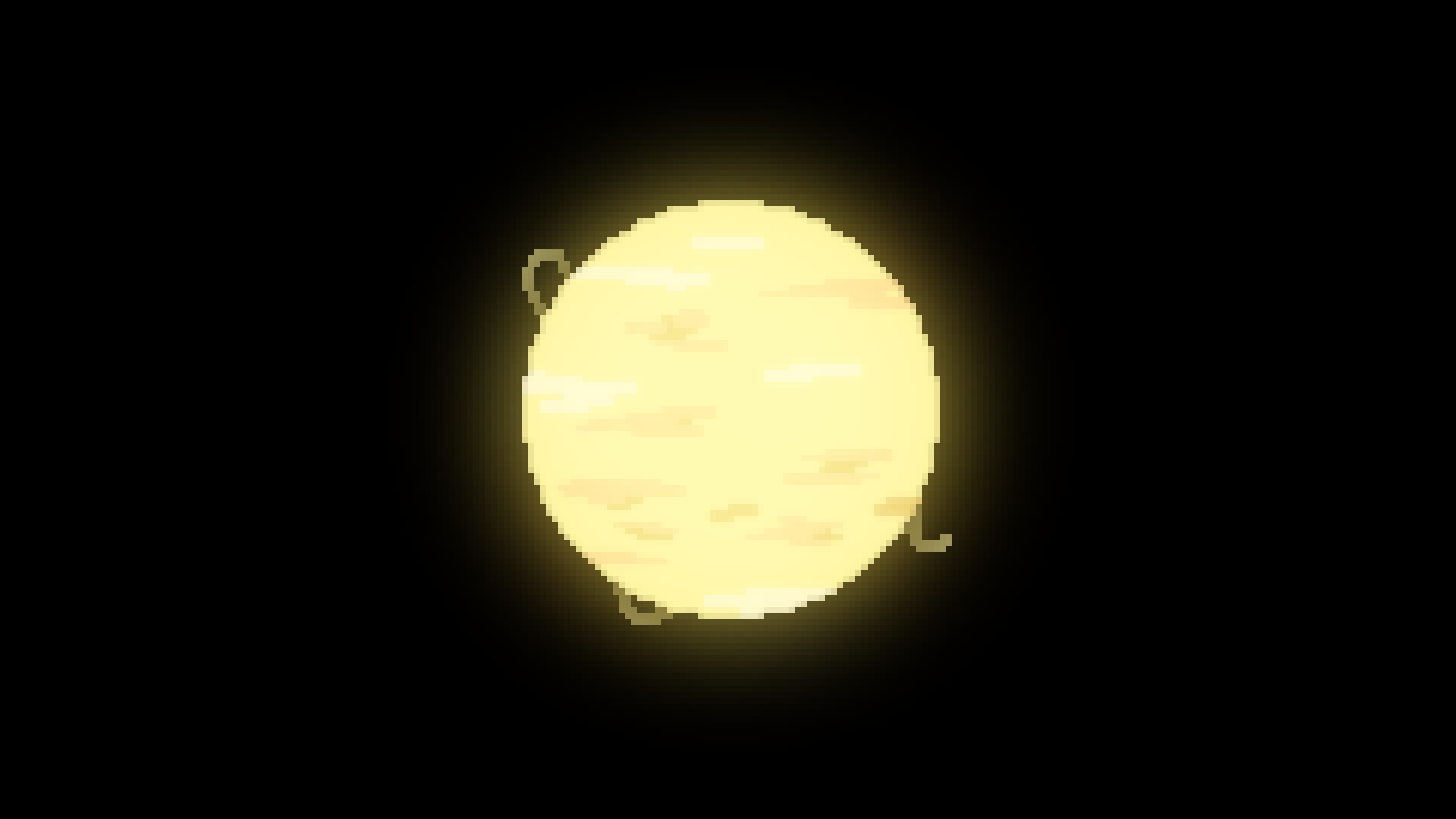

G type
{Star}
{Star}
Yellow Star
5,200*K - 7,000*K
0.6-1.5 solar luminocity
0.8-1.04 Solar masses
0.96-1.15 Solar radii
4 billion - 17 billion year lifespan
7.6% of all stars
5,200*K - 7,000*K
0.6-1.5 solar luminocity
0.8-1.04 Solar masses
0.96-1.15 Solar radii
4 billion - 17 billion year lifespan
7.6% of all stars
K type
{Star}
{Star}
Orange Star
3,700*K - 5,200*K
0.08-0.6 solar luminocity
0.45-0.8 Solar masses
0.7-0.96 Solar radii
17 billion - 70 billion year lifespan
12.1% of all stars
3,700*K - 5,200*K
0.08-0.6 solar luminocity
0.45-0.8 Solar masses
0.7-0.96 Solar radii
17 billion - 70 billion year lifespan
12.1% of all stars
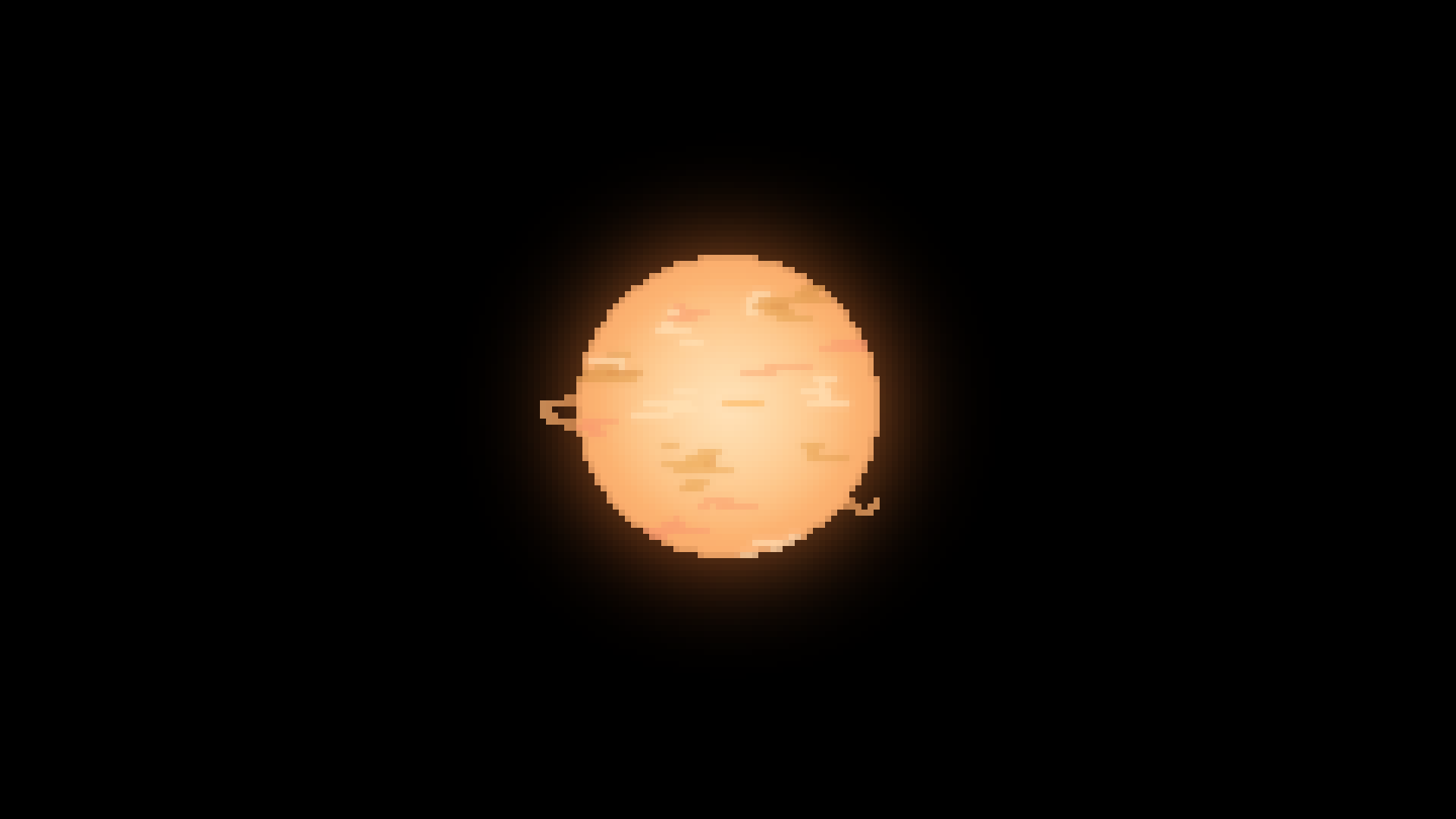

M type
{Star}
{Star}
Red Star
2,400*K - 3,700*K
0.08-0.01 solar luminocity
0.08-0.45 Solar masses
0.7- Solar radii
70 billion - 560 billion year lifespan
76.45% of all stars
2,400*K - 3,700*K
0.08-0.01 solar luminocity
0.08-0.45 Solar masses
0.7- Solar radii
70 billion - 560 billion year lifespan
76.45% of all stars
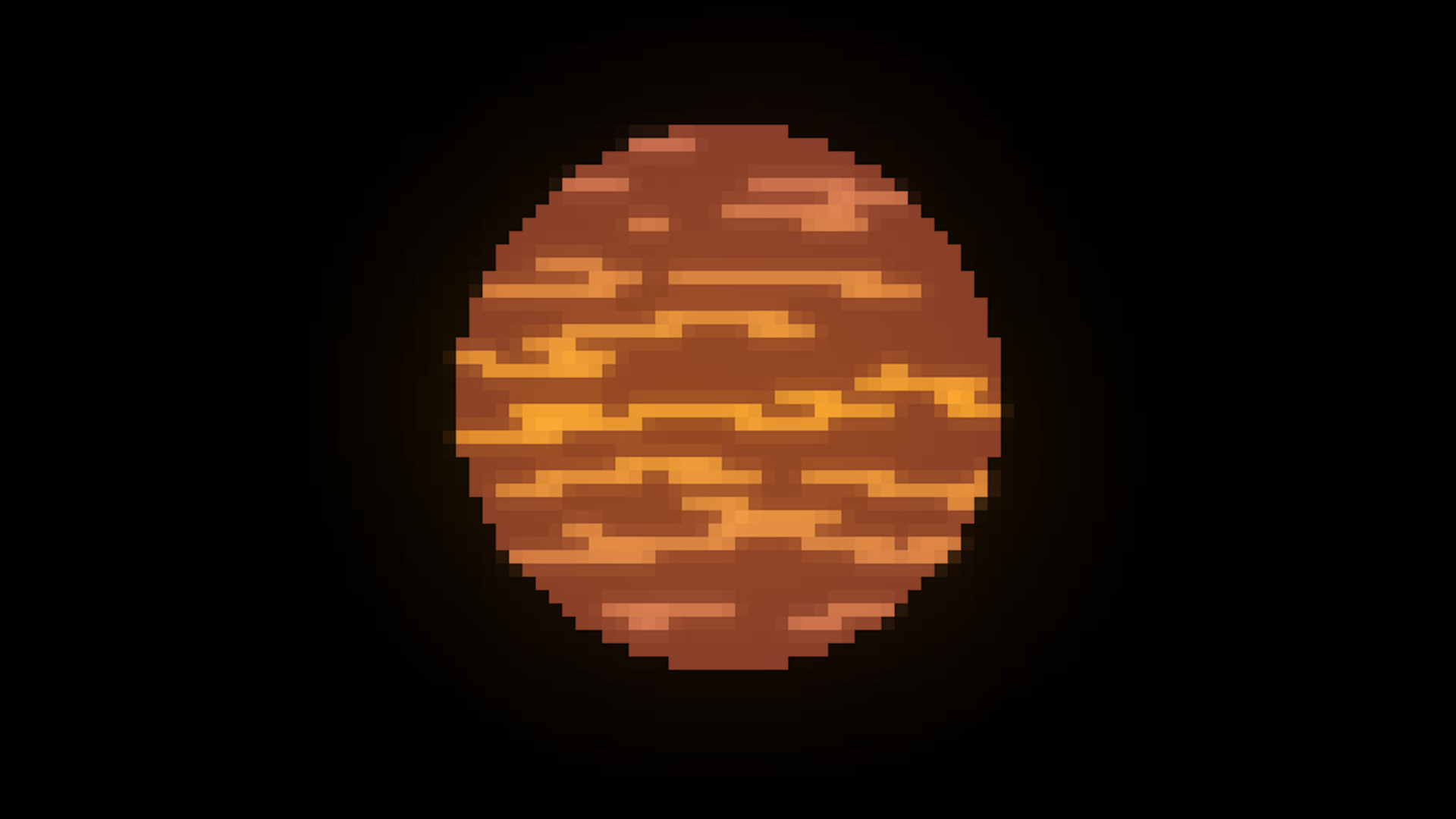

L type
{BD Star}
{BD Star}
Red Brown Dwarf Star
1,500*K - 2,400*K
0.01-0.0002 solar luminocity
65-90 Jupiter masses
1,500*K - 2,400*K
0.01-0.0002 solar luminocity
65-90 Jupiter masses
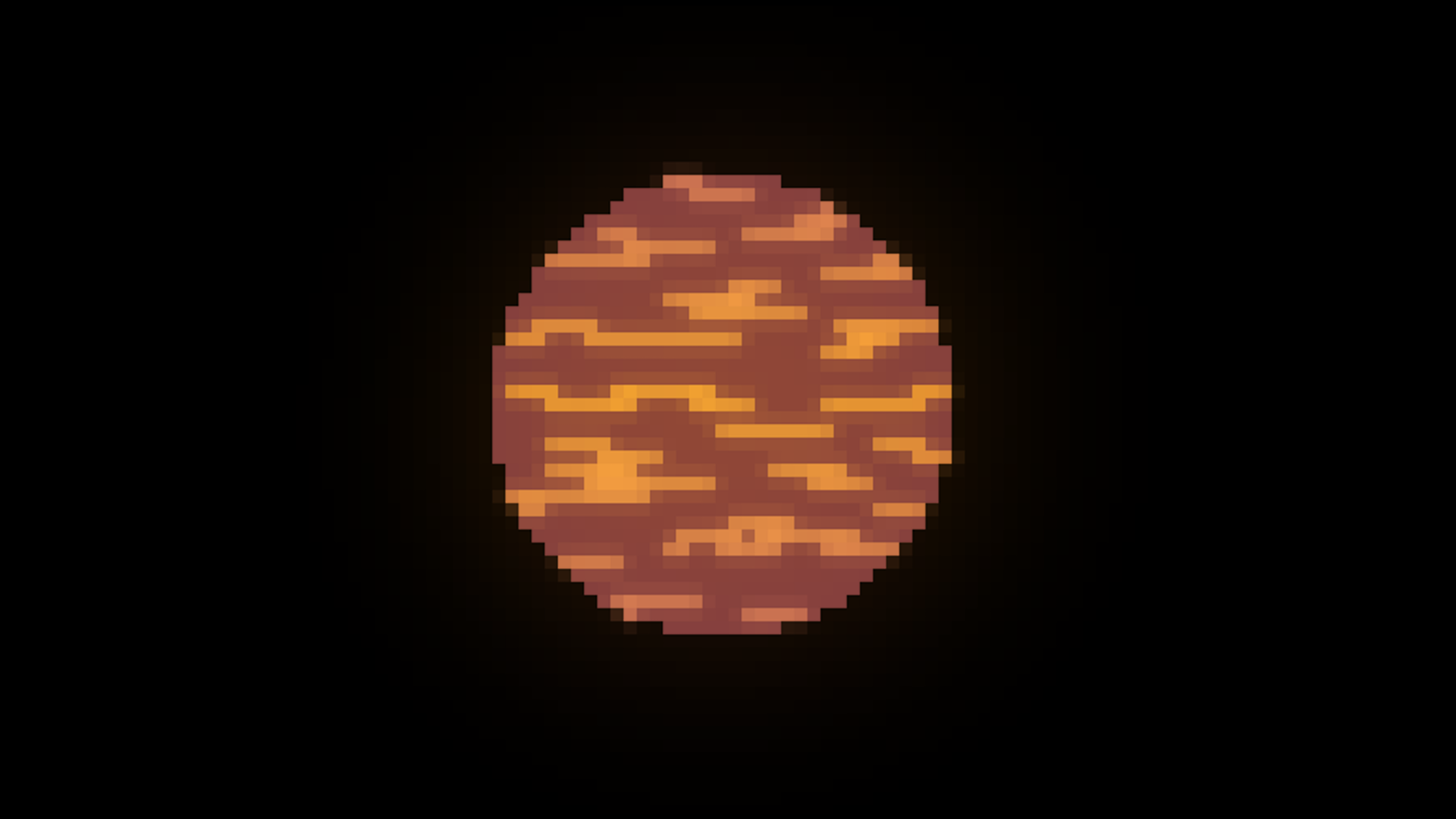

T type
{BD Star}
{BD Star}
Red-Brown Brown Dwarf Star
500*K - 1,500*K
0.0002-0.000005 solar luminocity
13 - 65 Jupiter masses
500*K - 1,500*K
0.0002-0.000005 solar luminocity
13 - 65 Jupiter masses
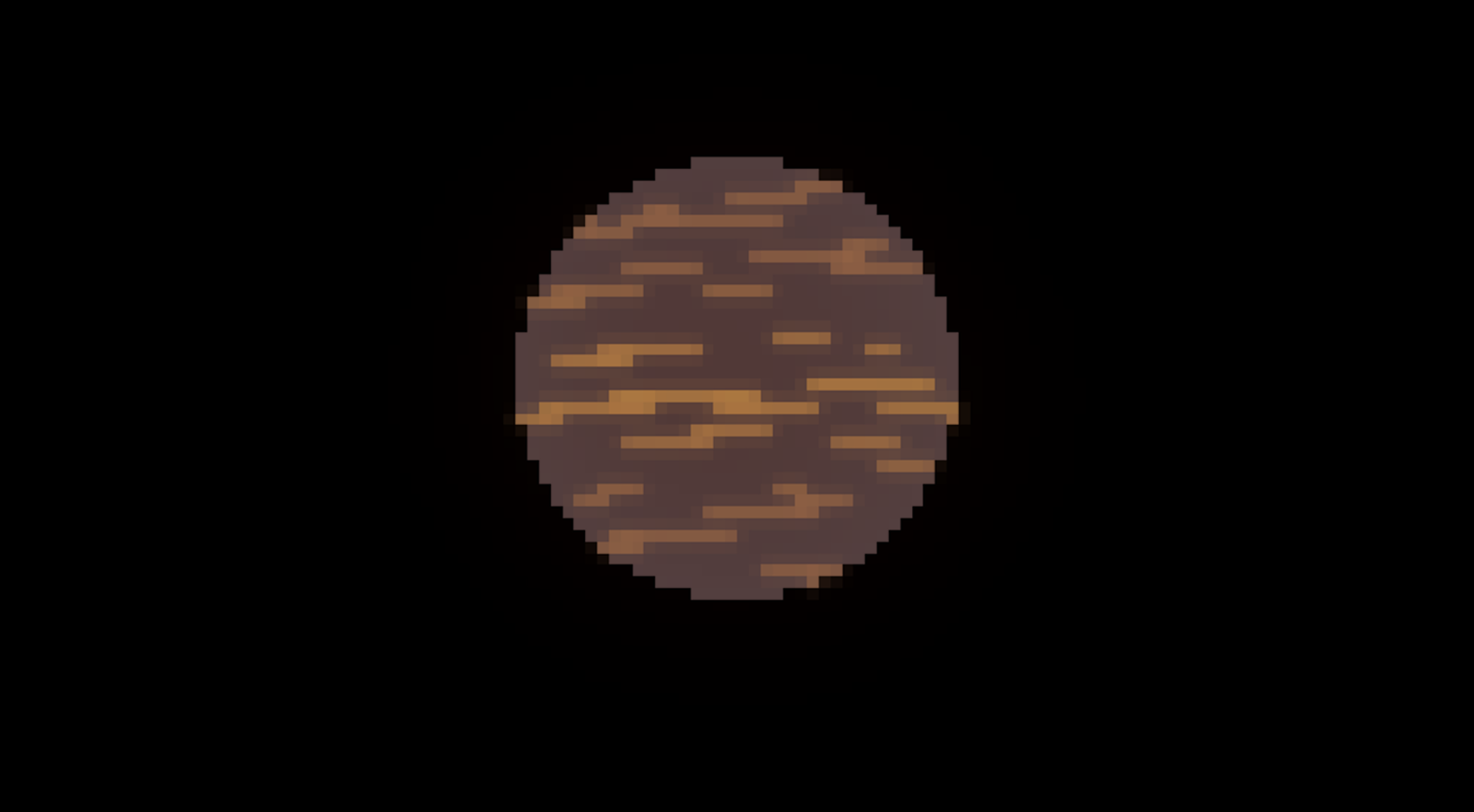

Y type
{BD Star}
{BD Star}
Brown Brown Dwarf Star
250*K - 500*K
0.000005- solar luminocity
13- Jupiter masses
250*K - 500*K
0.000005- solar luminocity
13- Jupiter masses

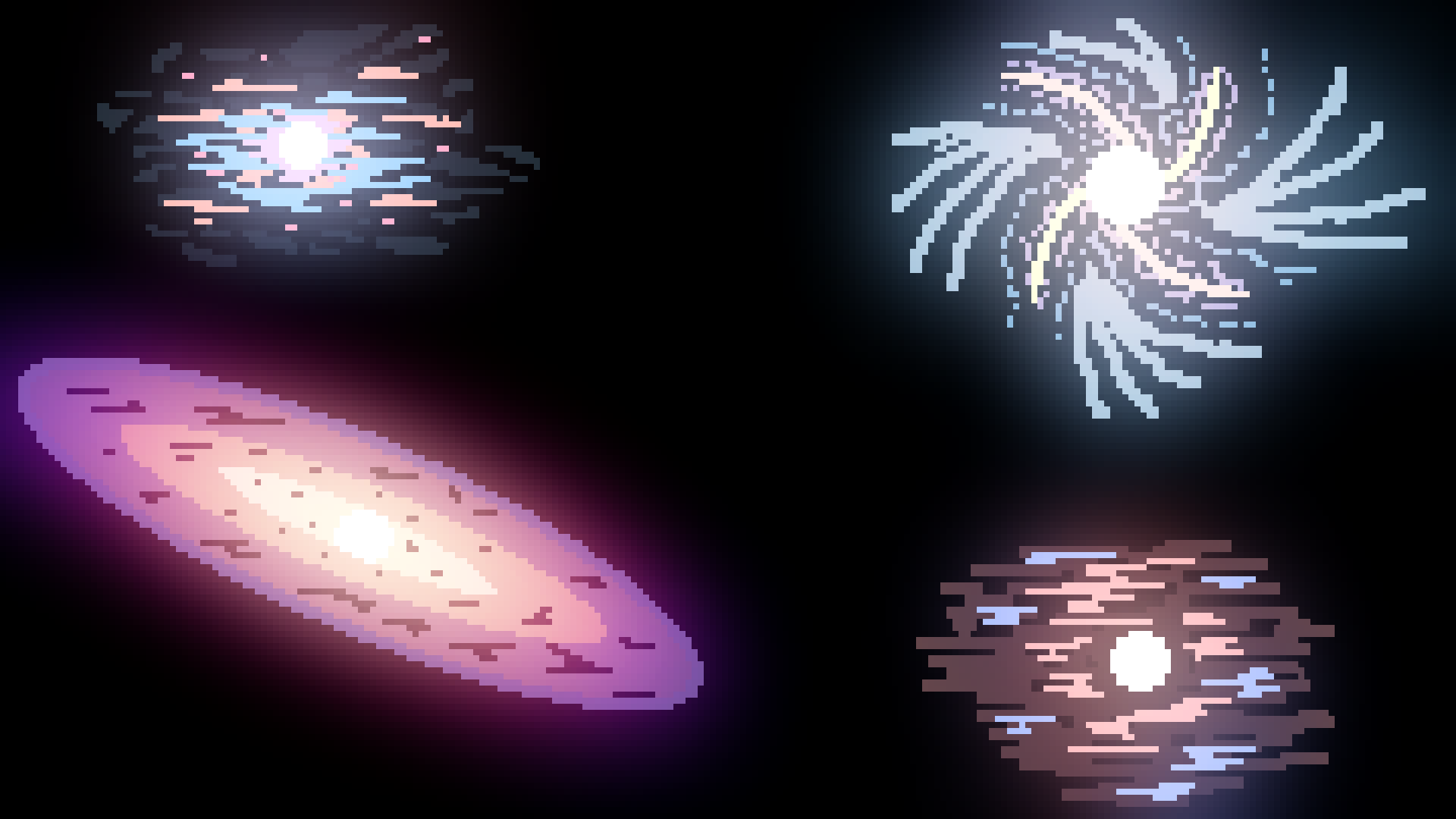
Spiral
{Galaxy}
{Galaxy}
A galaxy which consists of a core and spiral arms. Most of the stars orbit around the galaxy the same way on a plane with the arms around the center.
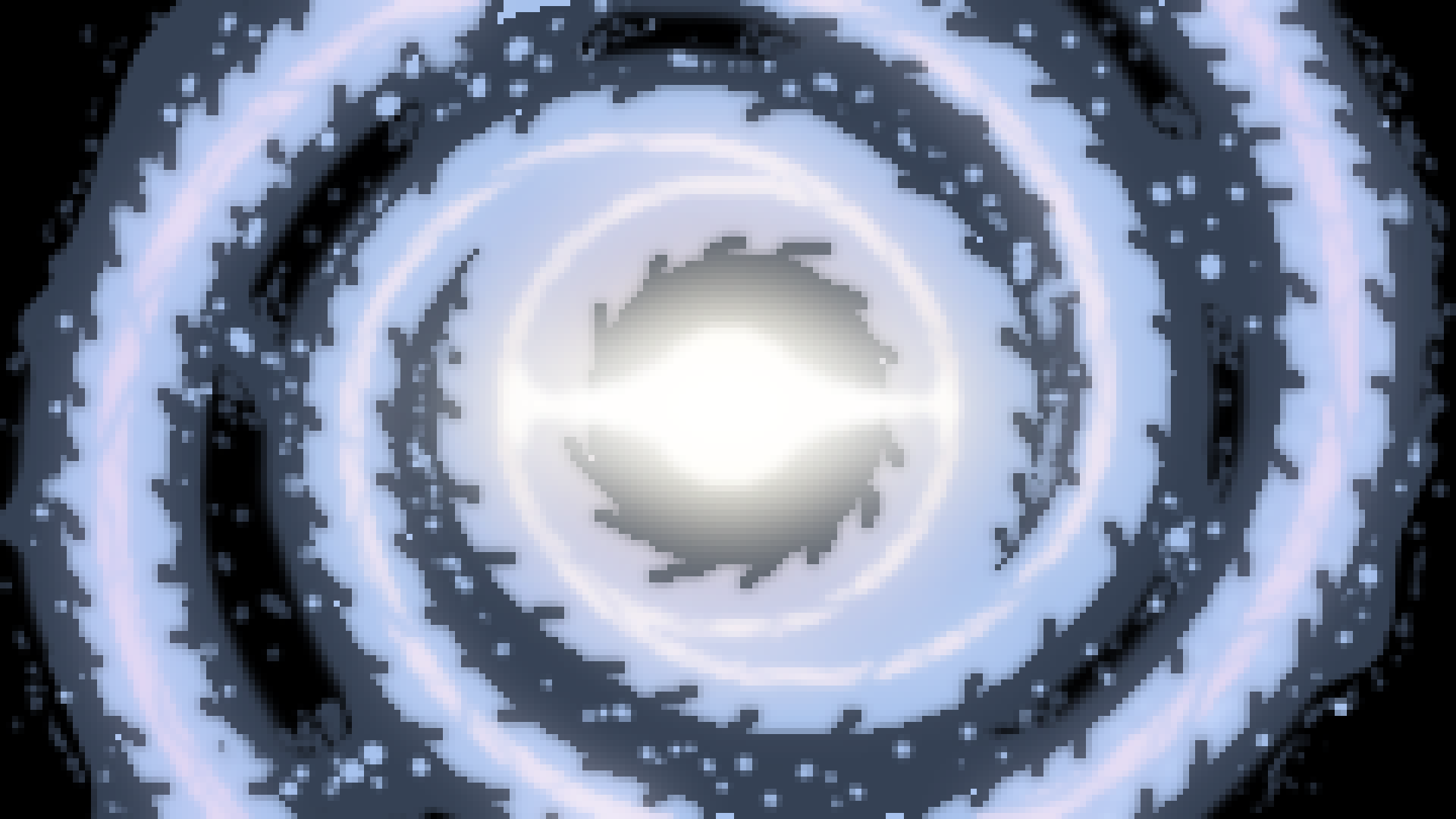
Barred Spiral
{Galaxy}
{Galaxy}
Very similar to a spiral galaxy except the arms are connected through one central bar extending through the center of the galaxy.
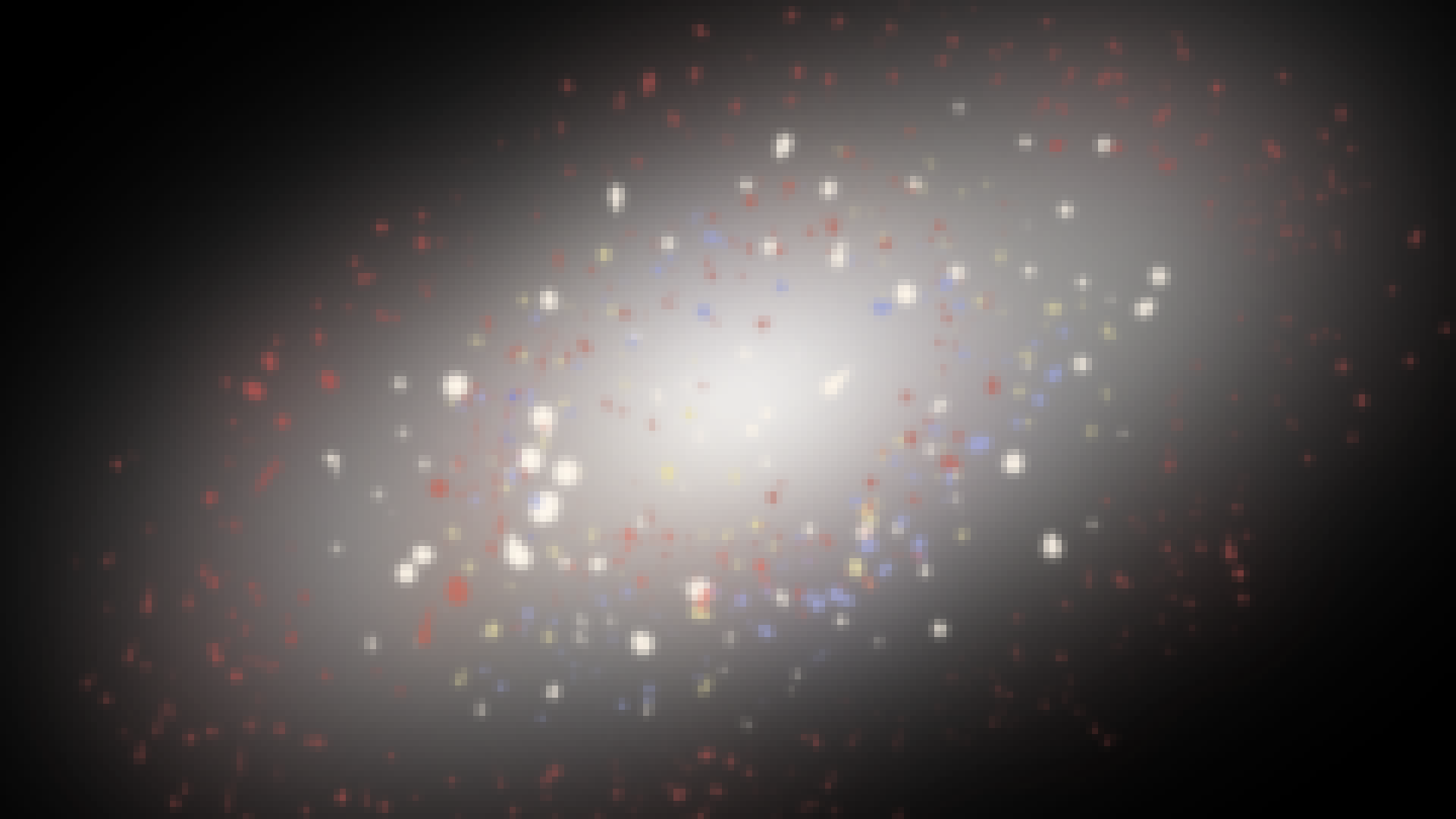
Eliptical
{Galaxy}
{Galaxy}
An eliptical galaxy has a center but no spiral arms. Instead all of the stars orbit freely around the galactic center. Small dwarf eliptical galaxies are called 'spheroidals'

Irregular
{Galaxy}
{Galaxy}
An irregular galaxy has no center and no order, it is a blob of gas and dust that contains many stars, but not as many as spirals or elipticals.
-Famous Bodies-

Hubble
Telescope
Telescope
The hubble space telescope is a satellite in low earth orbit. This telescope made some groundbreaking discoveries starting in 1990.

James Webb
Space
Telescope
Space
Telescope
The James Webb Space Telescope (JWST) is a state of the art telescope sent into outer space in late 2021.

International
Space
Station
Space
Station
The International Space Station (ISS) is an station in low earth orbit that more than 250 people have boarded from throughout the world.

Halley's
Comet
Comet
Hailey's comet is a comet that comes close to the earth every 76 years. It is very visible when it temporarily enters near earth orbit.

Vesta
Vesta is an asteroid in the main asteroid belt, it is the biggest asteroid we have found to date.

Oort Cloud
The Oort Cloud is a region of space around our solar system that contains billions to trillions of comets. Its borders are between 2,000 to 100,000 AU away from the sun.

UY Scuti
UY Scuti is one of the biggest stars we have found.

Stephenson
2-18
2-18
Stephenson 2-18 is considered to be the "biggest" star ever found, however the measurements are not exact so UY Scuti could still be bigger.

Sagittarius A*
Sagittarius A* is the supermassive black hole located at the center of the Milky Way Galaxy. It is about 4 million solar masses.

Messier 87
Messier 87 is a Hypermassive Black Hole located in a far away galaxy. It is the first blackhole people have ever imaged back in 2019.

TON 618
TON 618 is the largest black hole that we have found. It is over 40 billion solar masses.

Milky Way
The Milky Way Galaxy is the galaxy we are in, it has about 800 billion stars and is a spiral type galaxy.

Andromeda
The Andromeda Galaxy is 2.54 million light years away and the biggest galaxy in our local group. It has nearly 2 trillion stars and will merge with the Milky Way in a few billion years.

IC 1101
IC 1101 is the biggest galaxy we have found, consisting of nearly 100 trillion stars.
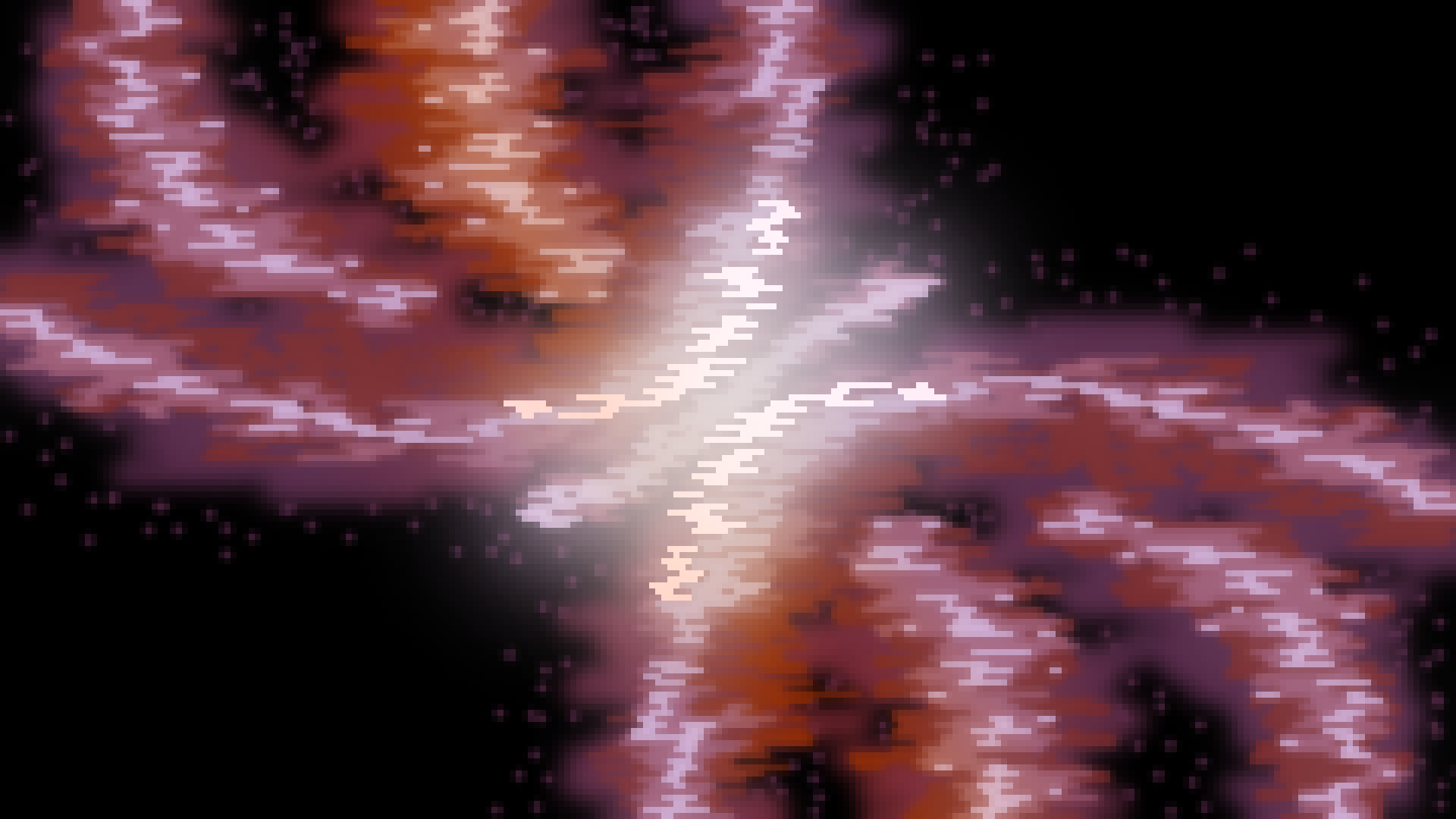
Orion Nebula
The Orion Nebula is a bright nebula located in the orion constellation. It stretches almost 25 light years across.
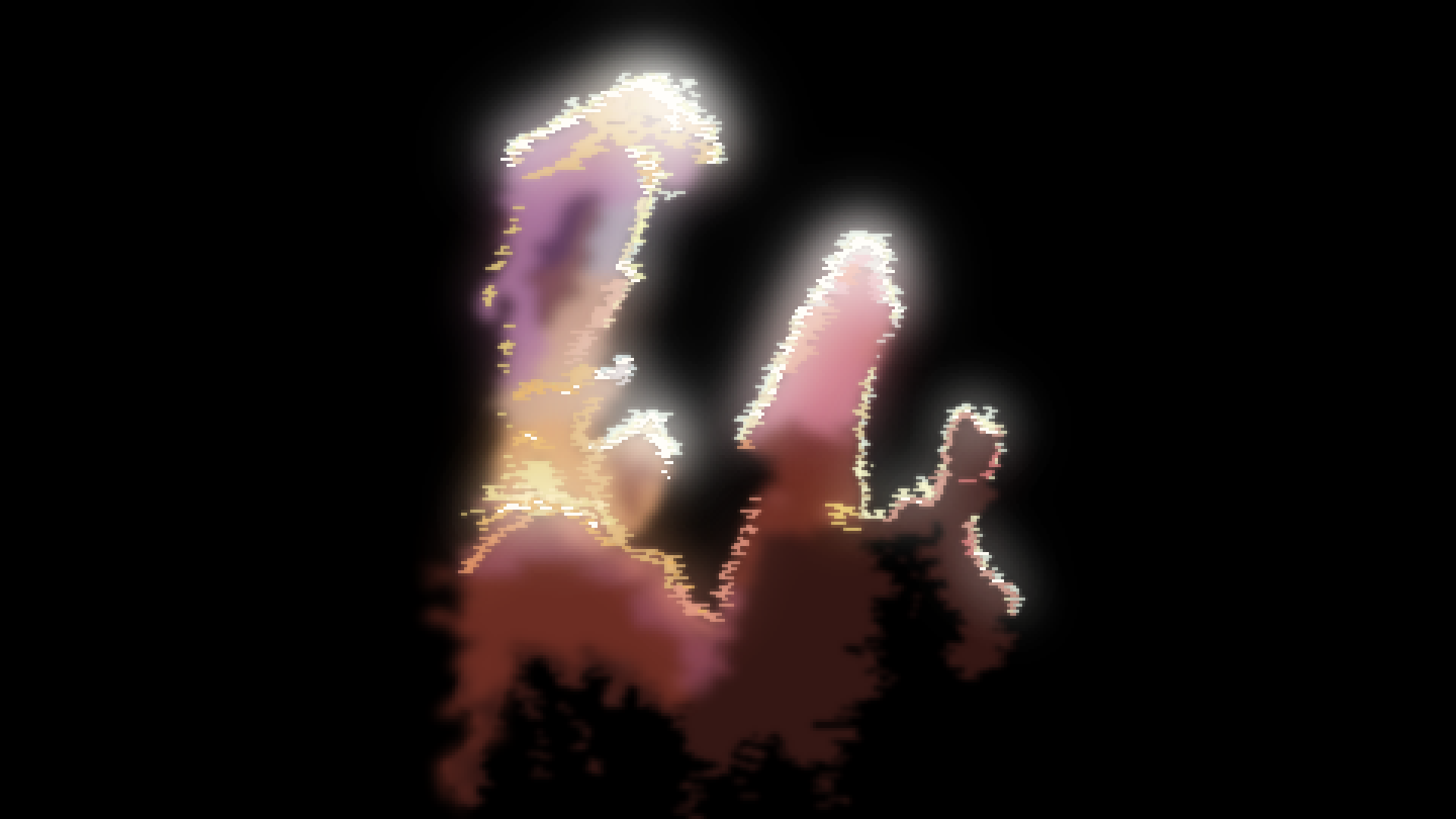
Pillars
Of Creation
Of Creation
The Pillars of Creation is a part of a nebula and known for its beauty. It spans almost 5 light years.

Virgo
Supercluster
Supercluster
The Virgo Supercluster is the supercluster of galaxies we are apart of. More than a thousand galaxies reside here.

Boötes Void
The Boötes Void is a very wide patch of space that contains next to nothing and is the biggest void we have found. It is 165 million light years across.